In an era where digital connectivity is integral to daily life, the release of Wi-Fi 8 promises to redefine our expectations for wireless communication. As technology evolves, consumers and industry stakeholders alike anticipate that Wi-Fi 8 will deliver unprecedented speeds, enhanced reliability, and broader coverage. To comprehend the significance of its upcoming launch, it is essential to explore the development history, technological innovations, deployment timelines, and practical implications associated with Wi-Fi 8. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the release process, empowering users to anticipate and leverage the advantages of this next-generation wireless standard effectively.
Understanding Wi-Fi 8: Evolution and Technological Breakthroughs

Wi-Fi standards have continually advanced to meet increasing bandwidth demands, facilitate seamless connectivity, and support the proliferation of connected devices. Starting from 802.11b in the late 1990s, each iteration has introduced significant improvements, culminating in Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and now setting sights on Wi-Fi 8 (802.11be). The development trajectory reflects an ongoing quest for higher throughput, ultra-low latency, and superior spectral efficiency.
Wi-Fi 8, also known as 802.11be, is designed to address the exponential growth in data consumption driven by streaming services, smart home devices, and enterprise applications. The technological innovations embedded within Wi-Fi 8 include wider channels—up to 320 MHz—multi-user MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) enhancements, and advanced modulation schemes like 4096-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation). These features collectively enable theoretical maximum data rates approaching 30 Gbps, a significant leap from previous standards.
In practical application, these improvements are projected to reduce latency to under 1 millisecond in optimal conditions, facilitating real-time gaming, augmented reality, and mission-critical IoT operations. The evolution from Wi-Fi 6 to Wi-Fi 8 is thus characterized by a focus on high-speed, reliable, and adaptive network performance, aligning with the demands of modern digital ecosystems.
Development Timeline and Industry Milestones Leading to Wi-Fi 8 Release
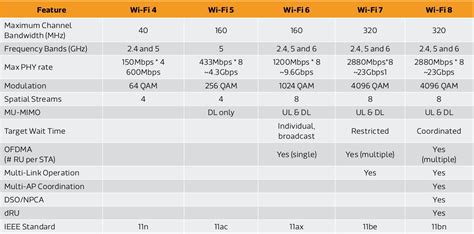
The development of Wi-Fi 8 is governed by the IEEE 802.11 Task Group, which establishes and ratifies wireless LAN standards. The process begins with proposal submission, followed by rigorous testing, interoperability assessments, and public review. Historically, each Wi-Fi iteration has taken approximately 3-4 years from initial proposal to widespread adoption.
Wi-Fi 8’s formal technological standard was finalized in late 2022, with preliminary industry certifications initiated in 2023. Major industry players, including Qualcomm, Intel, and Broadcom, have announced early prototype devices demonstrating Wi-Fi 8 capabilities. Commercial availability of Wi-Fi 8-compatible routers and client devices is projected to commence in late 2024 or early 2025, dependent on certification procedures and manufacturing scalability.
| Key Development Milestone | Estimated Timeline |
|---|---|
| Standard Ratification (IEEE 802.11be) | Late 2022 |
| Prototype Deployment and Testing | 2023-2024 |
| Initial Certification and Industry Readiness | Late 2024 |
| Commercial Launch and Device Availability | Early 2025 |

Anticipated Release Date and Factors Influencing Availability
The most precise projected release date for Wi-Fi 8 consumer devices hinges on multiple factors, including technological certification, manufacturing capacity, and market readiness. Based on current industry trajectories, the first wave of Wi-Fi 8 routers and client devices is expected to appear in the market during the first quarter of 2025.
Several industry analysts suggest that major global markets—North America, Europe, and Asia—will witness staggered deployments due to regional certification processes and regulatory standards. For instance, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States has already begun discussions regarding the spectrum allocations necessary for Wi-Fi 8 operation, aiming to streamline approvals.
However, factors such as supply chain disruptions, technological bugs during initial rollout, and carrier partnerships can influence the precise release schedules. It’s prudent for early adopters to monitor official announcements from device manufacturers and standardization bodies.
| Influencing Factors | Impact on Release Date |
|---|---|
| Certification Timeline | Potential delays if standards are not approved promptly |
| Manufacturing Capacity | Availability constrained by chip shortages or supply chain issues |
| Market Acceptance | Adoption rate could accelerate with early marketing efforts |
| Regulatory Approvals | Regional differences may cause staggered releases |
How to Prepare for the Wi-Fi 8 Launch: A Step-by-Step Guide
Preparing to upgrade to Wi-Fi 8 involves strategic planning, understanding device compatibility, and evaluating your current infrastructure. This step-by-step guide aims to enable consumers, IT professionals, and enterprise managers to efficiently transition to the next-generation wireless standard when it becomes available.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Network Infrastructure
Begin by auditing your existing Wi-Fi setup. Identify your current router model, supported standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6), and the capabilities of connected devices. Use network diagnostic tools to measure bandwidth, latency, and coverage. Recognizing limitations will inform your upgrade path and investment priorities.
Additionally, document the number of connected devices and their bandwidth requirements to determine whether your current hardware can support the enhanced performance Wi-Fi 8 promises—especially if you operate in high-density environments such as offices or smart-home setups.
Step 2: Stay Informed on Industry Developments and Certification Announcements
Regularly monitor updates from IEEE, Wi-Fi Alliance, and leading device manufacturers. Subscribing to industry newsletters, participating in tech forums, and attending relevant expos can provide early insights into product releases and certification milestones. Early knowledge enables timely procurement decisions.
Furthermore, check for firmware updates or compatibility advisories for existing hardware, as some devices may receive updates enhancing their support for upcoming standards, or at least prepare for seamless integration once compatible devices become available.
Step 3: Invest in Interim Hardware Upgrades
If your current equipment is outdated or incompatible with Wi-Fi 6, consider investing in routers that support at least Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax with extended spectrum). While these are not yet Wi-Fi 8 devices, they can enhance your network’s efficiency and provide future-proofing, ensuring smoother upgrades once Wi-Fi 8 hardware is accessible.
Remember that future Wi-Fi 8 routers are expected to be backward compatible, so maintaining flexibility in your infrastructure will optimize your investment returns.
Step 4: Budget for Future Purchases and Upgrades
Set aside financial resources for new devices when Wi-Fi 8 routers and clients enter the market. Anticipate higher costs initially due to advanced hardware features and limited early supply. Early adopters often pay a premium, but this can be offset by the benefits of superior speed and reliability.
Consider also the costs associated with upgrading network cabling, access points, and administrative software if deploying in commercial environments.
Step 5: Plan for Network Optimization and Security
Implement strategies for network security enhancements, including updated encryption protocols compatible with Wi-Fi 8. Equally important is planning for network segmentation and quality of service (QoS) configurations to maximize the benefits of higher throughput and lower latency.
Educate users on best practices to prevent network congestion and ensure optimal performance. Once Wi-Fi 8 devices are available, configuring them correctly from the outset will be crucial for harnessing their full potential.
Expected Benefits and Practical Applications of Wi-Fi 8

The advent of Wi-Fi 8 is set to revolutionize how we experience wireless connectivity, with tangible benefits spanning numerous sectors. Enhanced throughput could support ultra-high-definition streaming and large data transfers within seconds. Likewise, ultra-low latency will make real-time applications like cloud gaming, VR/AR, and telemedicine more responsive and reliable.
In industrial, smart city, and autonomous vehicle deployments, Wi-Fi 8’s improved spectral efficiency and interference mitigation mean more resilient networks capable of operating in challenging environments. Enterprises will benefit from increased capacity, enabling massive IoT device integrations without sacrificing performance.
Moreover, the integration of AI-driven network management tools will further optimize Wi-Fi 8 networks, dynamically adjusting configurations to maintain peak performance under changing conditions. By understanding the technological underpinnings and preparation strategies outlined here, users can position themselves to maximize these advantages immediately upon market entry.
Key Points
- Wi-Fi 8 offers significant speed, latency, and reliability improvements, fundamentally transforming wireless communication.
- Industry milestones suggest a commercial introduction of Wi-Fi 8 devices is likely in early 2025, subject to certification and manufacturing factors.
- Proactive assessment and hardware investments can ensure seamless transition and maximal benefit from Wi-Fi 8 deployment.
- Strategic planning around infrastructure upgrades and security measures will unlock the full potential of this next-generation standard.
- Early adoption can provide competitive advantages in both consumer and enterprise contexts, supporting future innovations.
What is the official release date for Wi-Fi 8?
+The first Wi-Fi 8-compatible devices are anticipated to launch in early 2025, following certification and industry readiness milestones achieved in late 2024.
Will existing devices support Wi-Fi 8?
+Most current devices will not support Wi-Fi 8 directly due to hardware limitations. However, routers supporting Wi-Fi 8 are expected to be backward compatible with earlier standards, allowing gradual migration.
How can I prepare my network for Wi-Fi 8?
+Assess your current hardware, stay informed about industry updates, consider interim upgrades like Wi-Fi 6E devices, and plan for future investments to ensure compatibility and optimized performance once Wi-Fi 8 becomes available.
What are the main benefits of Wi-Fi 8?
+Wi-Fi 8 promises faster data rates (up to 30 Gbps), lower latency (under 1 ms), increased network capacity, improved interference management, and broader coverage, supporting advanced applications across consumer, industrial, and enterprise domains.
Are there security concerns with Wi-Fi 8?
+Like all wireless standards, Wi-Fi 8 will incorporate robust security protocols, including advanced encryption methods. Staying updated with firmware and security patches remains essential to protect your network.
