

SpaceX
SpaceX wins NASA contract to launch Earth Observing System, but current administration has other plans
SpaceX recently snagged an $80.4 million NASA contract to launch an upcoming Earth-observing satellite sometime in 2022. That is, if the mission isn’t scrapped due to budgetary issues.
A used Falcon 9 rocket is slated to ferry the 3,748-lb. (1,700 kg) Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, and ocean Ecosystem satellite (aka PACE) to orbit sometime in December 2022. The mission, which provides data on oceans and particles in the atmosphere, is expected to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Its goal: to help us better understand our home planet. SpaceX is expanding its portfolio, after receiving certification for science launches in 2016. To date, SpaceX launched a bevy of scientific satellites including Jason-3 in 2106, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and GRACE-FO missions in 2018, and the upcoming Sentinel 6A in Nov. 2020.
But it’s been a tough journey for PACE. The satellite has been on the chopping block several times, but managed to avoid getting the ax so far.
That’s because the Trump administration has tried to cancel the ocean-watching mission three separate times now, in an effort to reduce the Earth science budget. Each time the president has tried to cut its funding, Congress voted to support it, including authorizing $131 million for the mission in December 2019.
So NASA has moved ahead with the development of the mission, and selected SpaceX as the launch provider on Feb. 4.
“SpaceX is honored to continue supporting NASA’s critical scientific observational missions by launching PACE, which will help humanity better understand, protect and preserve our planet,” Gwynne Shotwell, SpaceX’s president and chief operating officer, said in a company statement.
PACE will focus on our planet’s oceans, the clouds, and aerosols (small air particles) in an effort to better understand phytoplankton — tiny plant-like organisms in the ocean that are the base of the food chain. These organisms can tell us a lot about how climate change is affecting the environment.
“PACE will help scientists investigate the diversity of organisms fueling marine food webs and the U.S. economy, and deliver advanced data products to reduce uncertainties in global climate models and improve our interdisciplinary understanding of the Earth system,” NASA said in a statement.
“It will also continue systematic records of key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth’s climate,” officials wrote on the PACE mission’s website.
Like most plants, phytoplankton relies on chlorophyll to capture sunlight, and then using photosynthesis to turn it into chemical energy, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
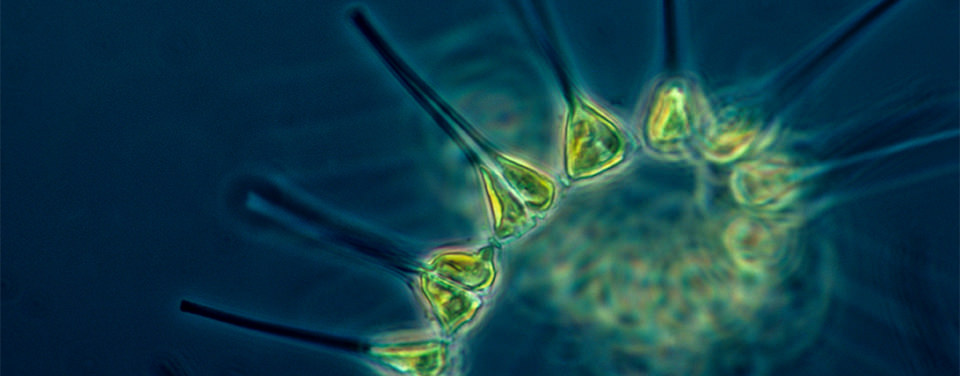
Phytoplankton are a diverse variety of species and their growth depends on the availability of things like carbon dioxide, sunlight, and nutrients. Just like their terrestrial counterparts, phytoplankton require can nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate, silicate, and calcium, depending on the species.
Other factors that influence growth rates are water temperature and salinity, water depth, wind, as well as what sort of predators are nearby.
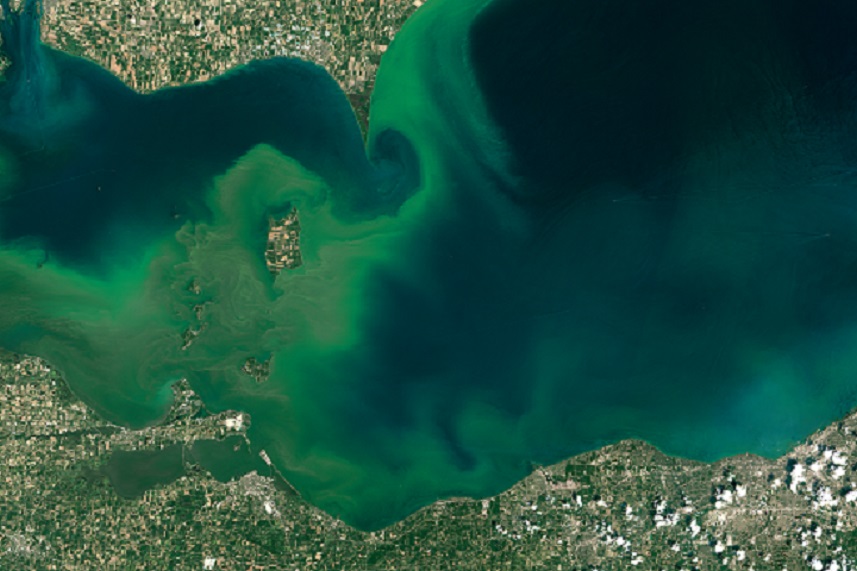
When conditions are just right, phytoplankton populations can grow explosively, a phenomenon we call a bloom. Blooms in the ocean may cover hundreds of square kilometers and are easily spotted in satellite imagery. A bloom may last several weeks, although the life expectancy of any individual organism is rarely more than a few days.
Phytoplankton are important because they are the foundation of the aquatic food web, feeding many different creatures from other microscopic organisms to enormous, mega-ton whales.
Phytoplankton aren’t always a good thing — certain species are known to produce powerful biotoxins, like the red tide. These toxic blooms can kill marine life and ultimately people if they accidentally eat contaminated seafood or by inhaling the organisms.

PACE’s primary tool is called the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI). It will measure the color of the ocean in a broad range of wavelengths, from ultraviolet to shortwave infrared, according to NASA. The satellite will observe the Earth from an orbital perch about 420 miles (675 kilometers) above the planet. (For reference, the space station orbits at 250 miles or 400 km up.)
“The color of the ocean is determined by the interaction of sunlight with substances or particles present in seawater, such as chlorophyll, a green pigment found in most phytoplankton species,” according to the mission’s website. “By monitoring global phytoplankton distribution and abundance with unprecedented detail, the OCI will help us to better understand the complex systems that drive ocean ecology.”
PACE will be in a sun-synchronous orbit, which will allow for consistent daylight conditions for imaging. This makes it easier for scientists to compare different regions and the same regions over long periods of time — if the satellite makes it to orbit.
Today, the president released his budget request for 2021, and once again, PACE is one of two Earth science missions he wants to cancel. Will its luck hold out? Will Congress vote to approve funding for the vital satellite despite the president’s suggestion? Only time will tell.
But with many coastal states recently suffering from red tide, this satellite will be a valuable tool in scientists’ arsenal to help them better understand these tiny organisms.
News
SpaceX and Elon Musk explain potential reasons for Starship loss

SpaceX and its CEO Elon Musk are starting to shed some light on the potential reasoning for the loss of Starship yesterday, which was lost after a successful launch and catch of the lower-stage booster.
Starship was lost during its ascension, and debris rained down over the Caribbean less than an hour after SpaceX lost all communication with the spacecraft.
A few hours after the launch was over, SpaceX started to shed some light after looking at preliminary data that the rocket left behind.
The company said that a fire developed in the aft section of Starship:
“Following stage separation, the Starship upper stage successfully lit all six Raptor engines and performed its ascent burn to space. Prior to the burn’s completion, telemetry was lost with the vehicle after approximately eight and a half minutes of flight. Initial data indicates a fire developed in the aft section of the ship, leading to a rapid unscheduled disassembly with debris falling into the Atlantic Ocean within the predefined hazard areas.”
Additionally, Musk said that there was some sort of oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall.
The leak was evidently large enough to build more pressure than the vent was able to handle:
🚨Elon Musk has also said an oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could be the cause of the anomaly. https://t.co/BgLkdA9Kk1
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 17, 2025
Some also seemed to recognize evidence of fires throughout the flight of Starship, which is obviously an anomaly:
Unconfirmed but what looks to be fire at the hinge of Starship’s flap. A potential RUD? We await as we get any confirmation from SpaceX.
They do not have comms with the spacecraft as this moment. pic.twitter.com/Cn1EF4AHpv
— Mihir Tripathy (@mihirneal) January 16, 2025
There will be more information regarding the loss of Starship in the coming days and weeks, but Musk already believes that a bit of fire suppression and more volume in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could fix the issue.
“Nothing so far suggests pushing next launch past next month,” he said, so Flight 8 could happen sometime in February.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
SpaceX completes second catch of lower stage, but loses Starship

SpaceX completed its seventh launch of Starship on Thursday, accomplishing a clean liftoff and catch of the first-stage booster. However, the upper stage was lost after its ascent.
The launch took place just a few minutes after 5 p.m. on the East Coast, as the first attempts at getting Starship in the air for the seventh time were delayed by weather both last week and this week.
Conditions were favorable on Thursday as SpaceX looked to follow up a successful campaign by Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos’s company, earlier today.
SpaceX went into the seventh Starship launch with plans for a catch attempt of the first-stage booster, something it attempted and completed during the fifth test launch last year. It decided to skip a catch attempt with the sixth test flight as conditions were not aligned.
For now, SpaceX is extremely selective as to when it attempts catches.
However, it was successful during this attempt, its second completed catch:
🚨 🚀 Here is @SpaceX’s full catch of the Lower Stage Booster from Starship Flight 7! pic.twitter.com/IXIRAGr1Md
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
This flight differed from previous launches as SpaceX rolled out several improvements to the rocket and the processes as it featured plans to do a Starlink deployment simulation and had various adjustments to flap placement and avionics.
These plans were disrupted by the fact that SpaceX lost all communications with Starship about ten minutes into the flight, which the aerospace company confirmed was a result of losing the spacecraft sometime during its ascent.
🚀🚨 Telemetry on Starship has been lost. All comms with the ship have been lost, and SpaceX’s livestream says this is an “anomaly.”
“We are assuming the ship has been lost.” pic.twitter.com/fyyCNuXVRg
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
Although the catch was successful, the loss of the actual rocket seemed to be a huge damper on the entire event. SpaceX confirmed several minutes after the loss of communications that the rocket was destroyed and was lost.
It was its first failure since the second Starship launch in November 2023. SpaceX had no answers for why the rocket was destroyed and lost.
We will keep you updated in the coming days.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
SpaceX confirms next Starship launch target – Here’s when it will take off

SpaceX has confirmed a new target date for the seventh Starship test launch after weather in Texas delayed the first scheduled date for “three or four days.”
The company is now targeting the launch for Monday, January 13, at 4 p.m. CST or 5 p.m. EST. The launch date is not set in stone as any variety of delays could impact this, but SpaceX hopes to finally take off after a delay that pushed it back from January 10.
🚨 STARSHIP LAUNCH DATE: @SpaceX says Starship’s 7th test flight is now targeted for Monday, January 13 at 4pm CST
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 8, 2025
What’s new with this Starship launch
With this being the seventh test launch of Starship, there are several things that the company will change and hope to accomplish. All of these launches are done in preparation for eventually taking flight to Mars, something that will happen next year, according to CEO Elon Musk.
First, SpaceX is rolling out a next-generation ship with “significant upgrades.” Forward flaps have been made smaller and are repositioned away from the heat shield, which will “reduce their exposure to reentry heating.”
There is also a 25 percent increase in propellant volume, a new fuel feedline system for the Raptor vacuum engines, and a better-than-ever propulsion avionics module that will control the valves and reading sensors.
Avionics, as a whole, underwent a redesign and now have more capability and redundancy for missions as they become more complex.
Starlink test
SpaceX is also planning to deploy 10 Starlink simulators that are similar in size and weight to the next-generation Starlink satellites:
“While in space, Starship will deploy 10 Starlink simulators, similar in size and weight to next-generation Starlink satellites as the first exercise of a satellite deploy mission. The Starlink simulators will be on the same suborbital trajectory as Starship, with splashdown targeted in the Indian Ocean. A relight of a single Raptor engine while in space is also planned.”
Ship return and catch
There will be several experiments that have to do with returning Starship and various catch scenarios and sequences. One of which will see “a significant number of tiles be removed to stress-test vulnerable areas across the vehicle.”
The ship’s reentry profile was also intentionally designed to test the structural limits of the flaps while at the point of maximum dynamic pressure during reentry.
Currently, SpaceX did not detail whether it would attempt another catch during this test launch. These are usually game-time decisions.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.


















