SpaceX
SpaceX Falcon Heavy completes successful rehearsal, static fire pushed back due to bug in launch pad hardware
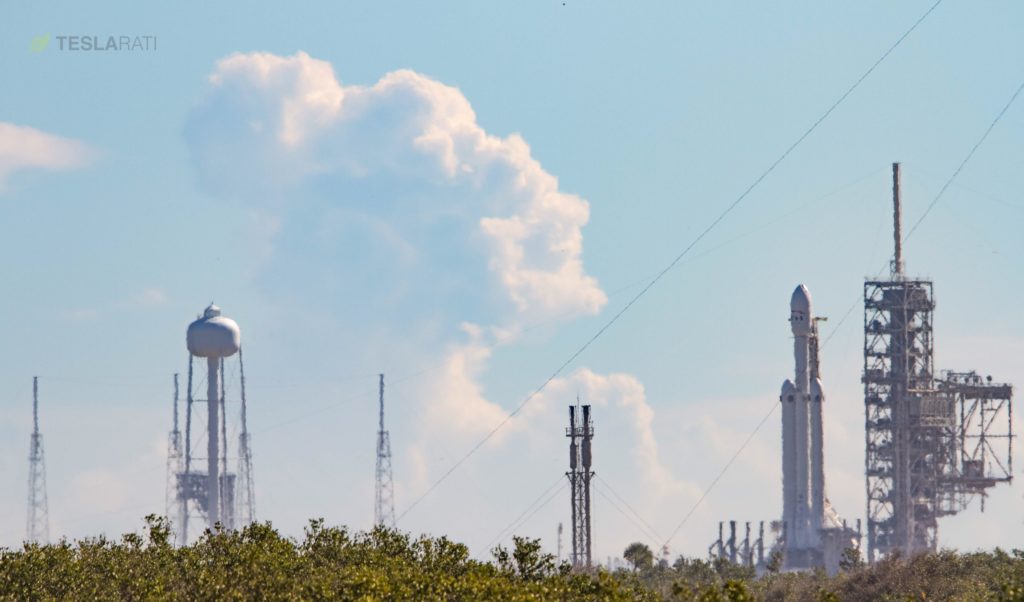
More than a decade after its 2005 public conception, SpaceX is closer than ever to the first launch Falcon Heavy, the company’s newest rocket. Earlier this afternoon, the vehicle was aiming for its first static fire test, in which all 27 of its engines would be ignited (nearly) simultaneously in order to test procedures and the rocket itself. This attempt was sadly scrubbed, but only after the vehicle apparently completed a successful wet dress rehearsal, which saw Falcon Heavy fully loaded with propellant. According to Orlando’s News 13, the attempt was scrubbed only after one of eight hold-down clamps showed signs of bugs.

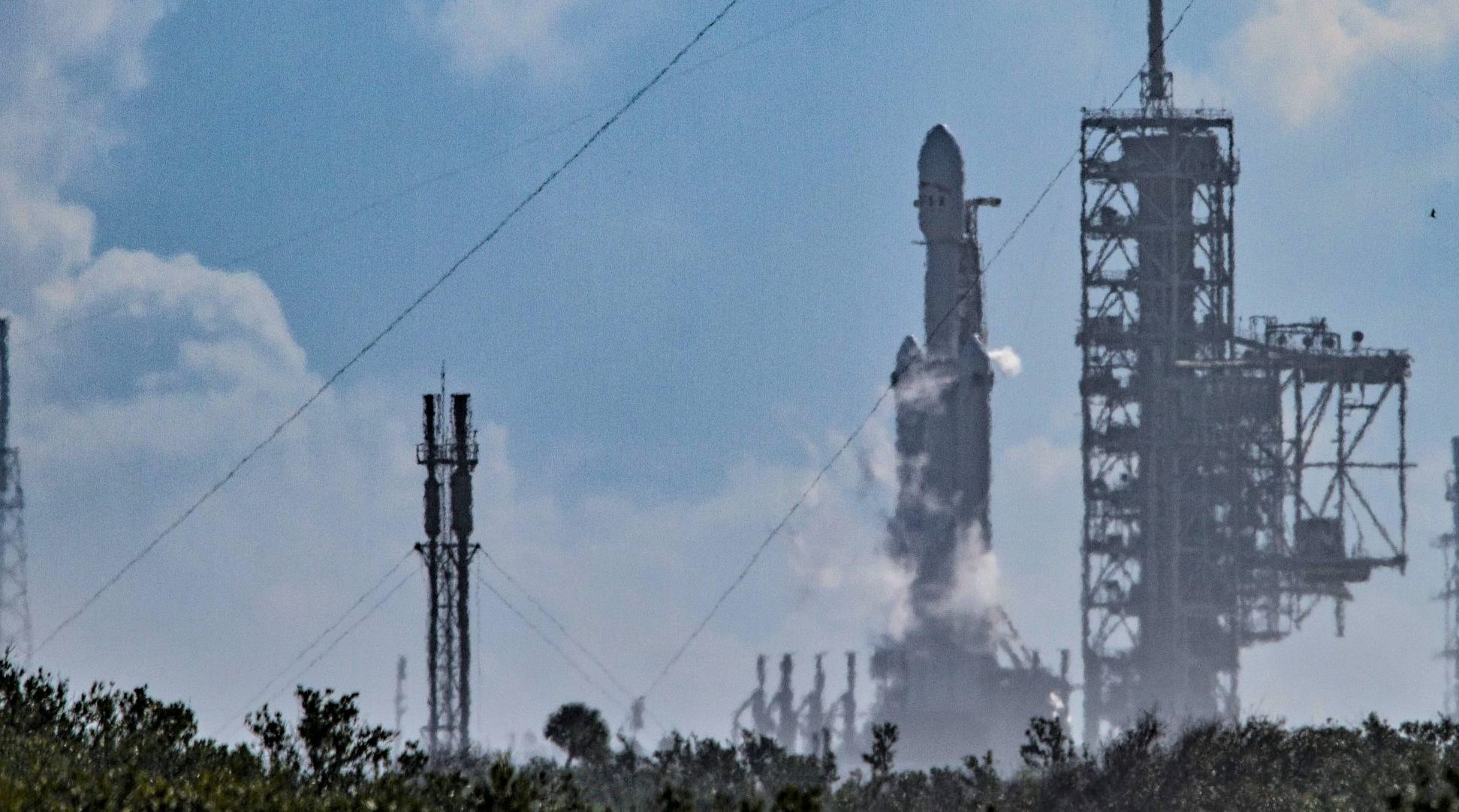
Falcon Heavy vertical at Pad 39A on Thursday, January 11. After a successful rehearsal, the static fire was scrubbed due to a small hardware bug. (Tom Cross/Teslarati)
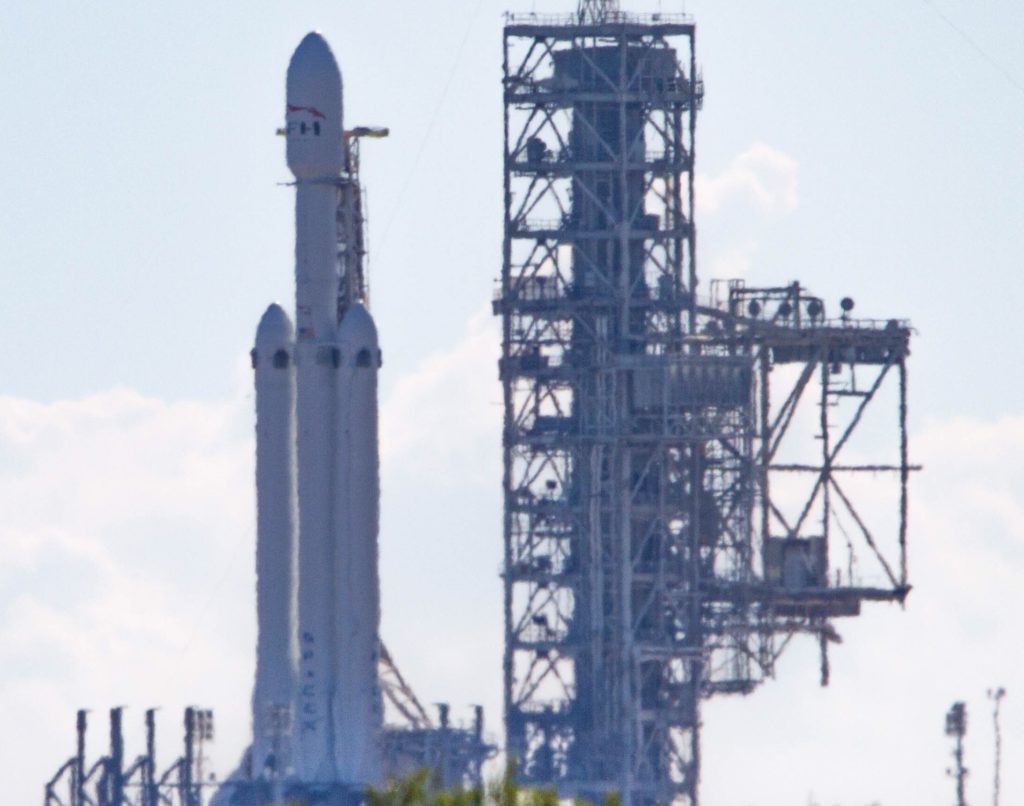

Falcon Heavy vertical at Pad 39A on Thursday, January 11. After a successful rehearsal, the static fire was scrubbed due to a small hardware bug. (Tom Cross/Teslarati)
While Falcon Heavy is not explicitly critical for SpaceX’s near-term launch business and its loftier future goals, the development and operation of such a massive launch vehicle will likely serve as a strong foundation as the company transitions more aggressively into the design, engineering, and manufacture of its still-larger BFR series of rocket boosters and upper stages. Falcon Heavy stands approximately as tall as Falcon 9 at around 70 m (230 ft), but features three times the thrust and a little less than three times the weight of SpaceX’s workhorse rocket. With 27 Merlin 1D engines to Falcon 9’s namesake nine, Falcon Heavy’s 22,800 kN (5,000,000 lbf) of thrust is a nearly inconceivably amount of power, equivalent to twenty Airbus A380 passenger jets at full throttle.
Why is Falcon Heavy important?
If SpaceX manages to pull off Falcon Heavy as a successful and reliable launch vehicle on the order of its reasonably successful Falcon 9, BFR may well be an easier vehicle to develop and operate, thanks to its single-core design. As Musk himself has discussed over the last year or so, the problem of safely and reliably distributing the thrust of Heavy’s side cores to the center core was unexpectedly difficult, as were the issues of igniting all 27 Merlin 1Ds and safely separating the side cores while in flight. Ultimately, the payload improvement (while in a fully reusable mode of operation) was quite small, particularly for the geostationary missions that make up essentially all prospective Falcon Heavy customer missions.
The additional complexity of recovery and refurbishing three separate Falcon 9 boosters almost simultaneously likely serves to only worsen the vehicle’s potential payoff, although the upcoming Block 5 iteration of Falcon 9 may partially improve the vehicle’s ease of operation. If Block 5 is indeed as reusable as SpaceX intends to make it, then a handful of Block 5 Falcon Heavy vehicles could presumably maintain a decent launch cadence for the vehicle without requiring costly and time-consuming shipping all over the continental US.
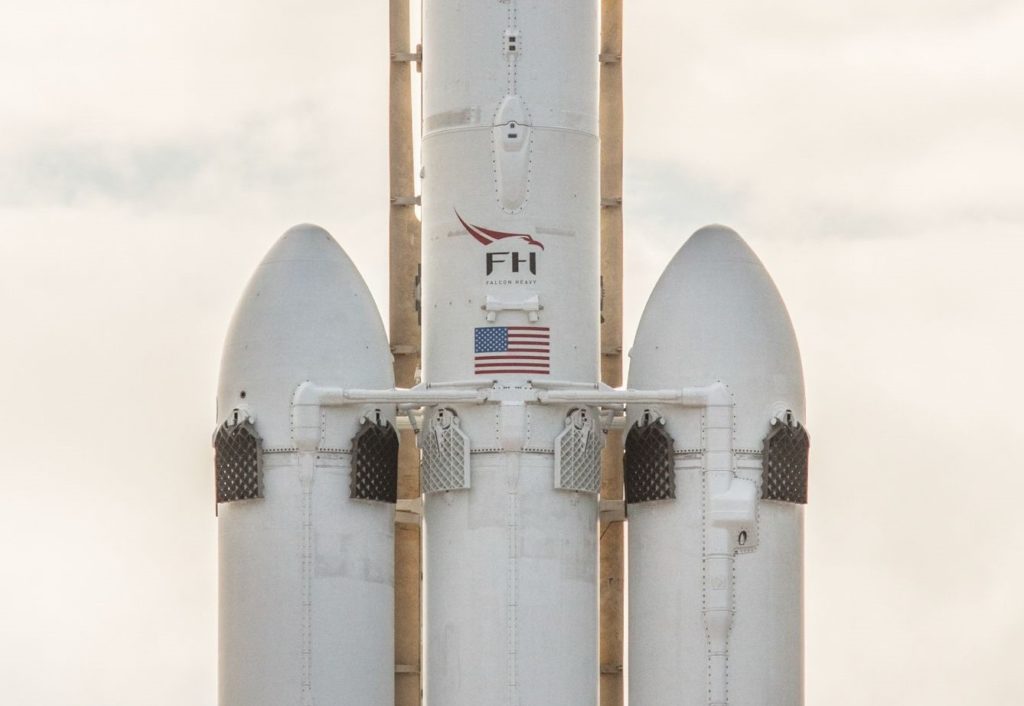

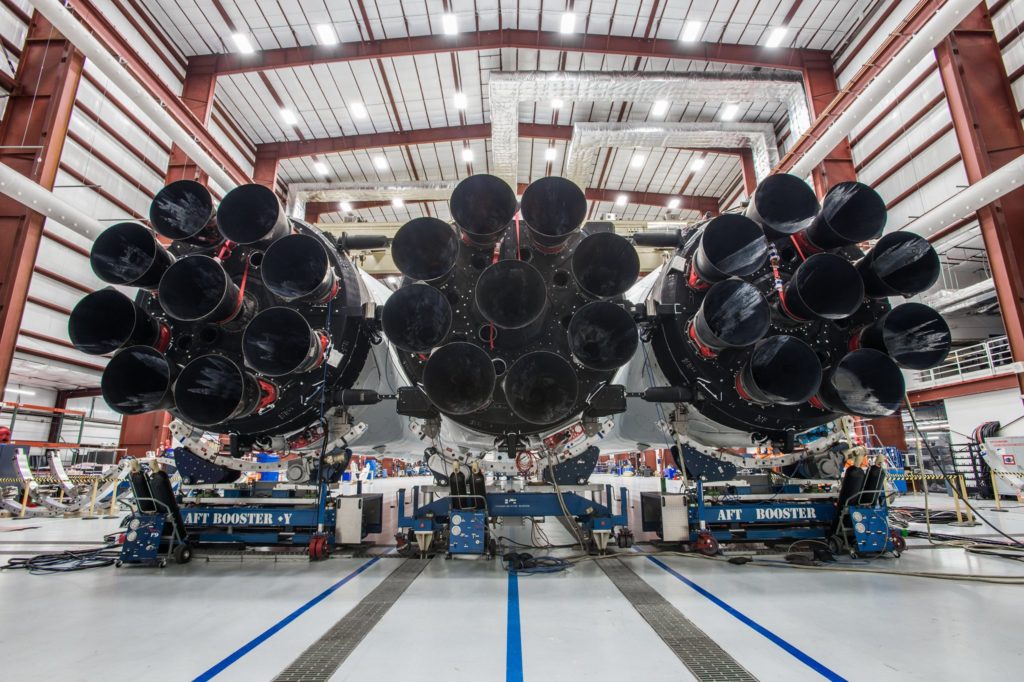
A closeup of Falcon Heavy’s three first stages, all featuring grid fins. The white bars in the center help to both distribute stress loads and separate the side cores from the center booster after launch. (SpaceX)
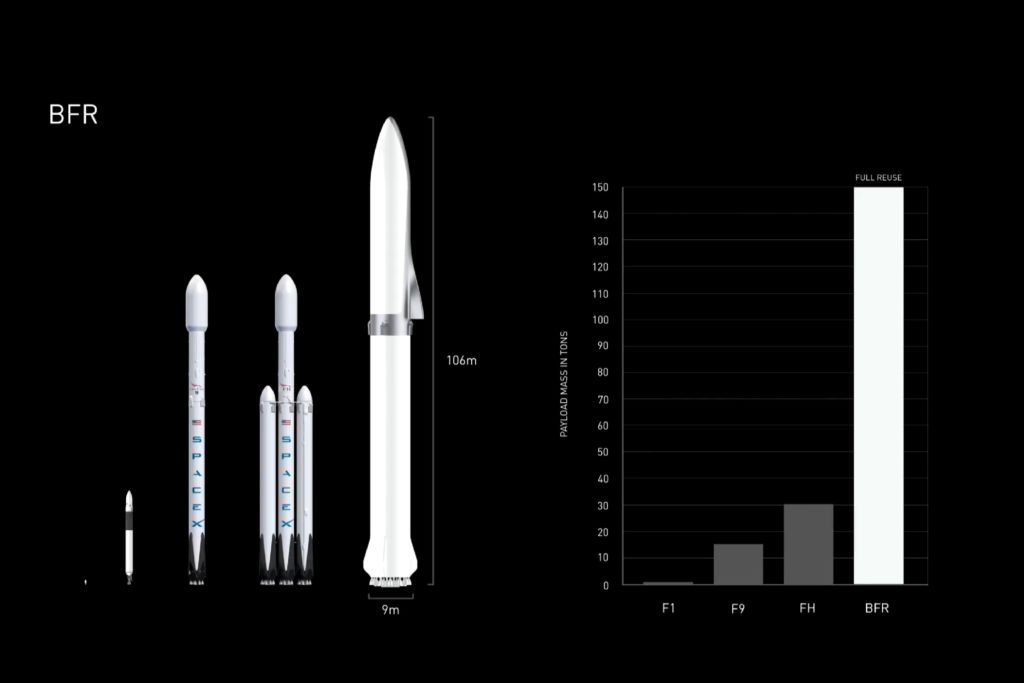
Nevertheless, the (hopefully successful) experience that will follow the launch and recovery operation of a super heavy-lift launch vehicle (SHLV) with ~30 first stage engines will be invaluable for SpaceX’s interplanetary goals. While BFR will be free of the complexity Falcon Heavy’s triple-core first stage added, it is still a massive vehicle that absolutely dwarfs anything SpaceX has attempted before. BFR in its 2017 iteration would mass around three times that of Falcon Heavy and feature 30 Raptor engines capable of approximately 53,000 kN (12,000,000 lbf) of thrust at liftoff, around 2.5x that of Heavy. Many, many other features mean that BFR and particularly BFS will be extraordinarily difficult to realize: BFS alone will be treading into truly unprecedented areas of spaceflight with the scale, longevity, and reusability it is intended to achieve while comfortably ferrying dozens of astronauts to and from Mars and the Moon.
However, the scale of BFR is equivalent to that of the famous Saturn V rocket that took astronauts to the Moon in the 1960s and 70s. In other words, while still dumbfoundingly massive and unprecedented in the modern era, rockets at the scale of BFR do in fact have a precedent of success, which lends the effort considerable plausibility, at least at proof-of-concept level. As of September 2017, Elon Musk suggested that SpaceX was aiming to begin construction of the first BFS (Big ____ Spaceship) by the end of Q2 2018, a truly Muskian deadline that probably wont hold. Still, if construction of the first prototype begins at any point in 2018, it will bode well for SpaceX’s aggressive timelines.
- Falcon Heavy’s three boosters and 27 Merlin 1D engines on full display. (SpaceX)
- BFR shown to scale with Falcon 1, 9, and Heavy. (SpaceX)
- .While SpaceX’s own visualizations are gorgeous and thrilling in their own rights, Romax’s interpretation adds an unparalleled level of shock and awe. (SpaceX)
In the meantime, BFR’s precursor Falcon Heavy has effectively completed its first wet dress rehearsal, although the static fire attempt was scrubbed for the day. This is understandable for such a complex and untested vehicle, especially after SpaceX’s exceptionally quick modifications to Pad 39A. While unofficial, word is that an issue with one of the Transport/Erector/Launcher’s (TEL) eight separate launch clamps caused the scrub. Those launch clamps ensure that the massive vehicle would stay put during a static fire, and the status of those clamps would be especially important during such an unusually long static fire of such a powerful rocket.
Stay tuned for updates on SpaceX’s upcoming launches and Falcon Heavy’s next static fire attempt, likely within the next several days. The vehicle’s inaugural launch date is effectively up in the air until the static fire has been successfully completed, but as of yesterday SpaceX was understood to be targeting January 26th. Delays are to be expected.
Follow along live as Teslarati’s launch photographer Tom Cross weathers the delays and covers the static fire attempt live from Cape Canaveral.
News
SpaceX and Elon Musk explain potential reasons for Starship loss
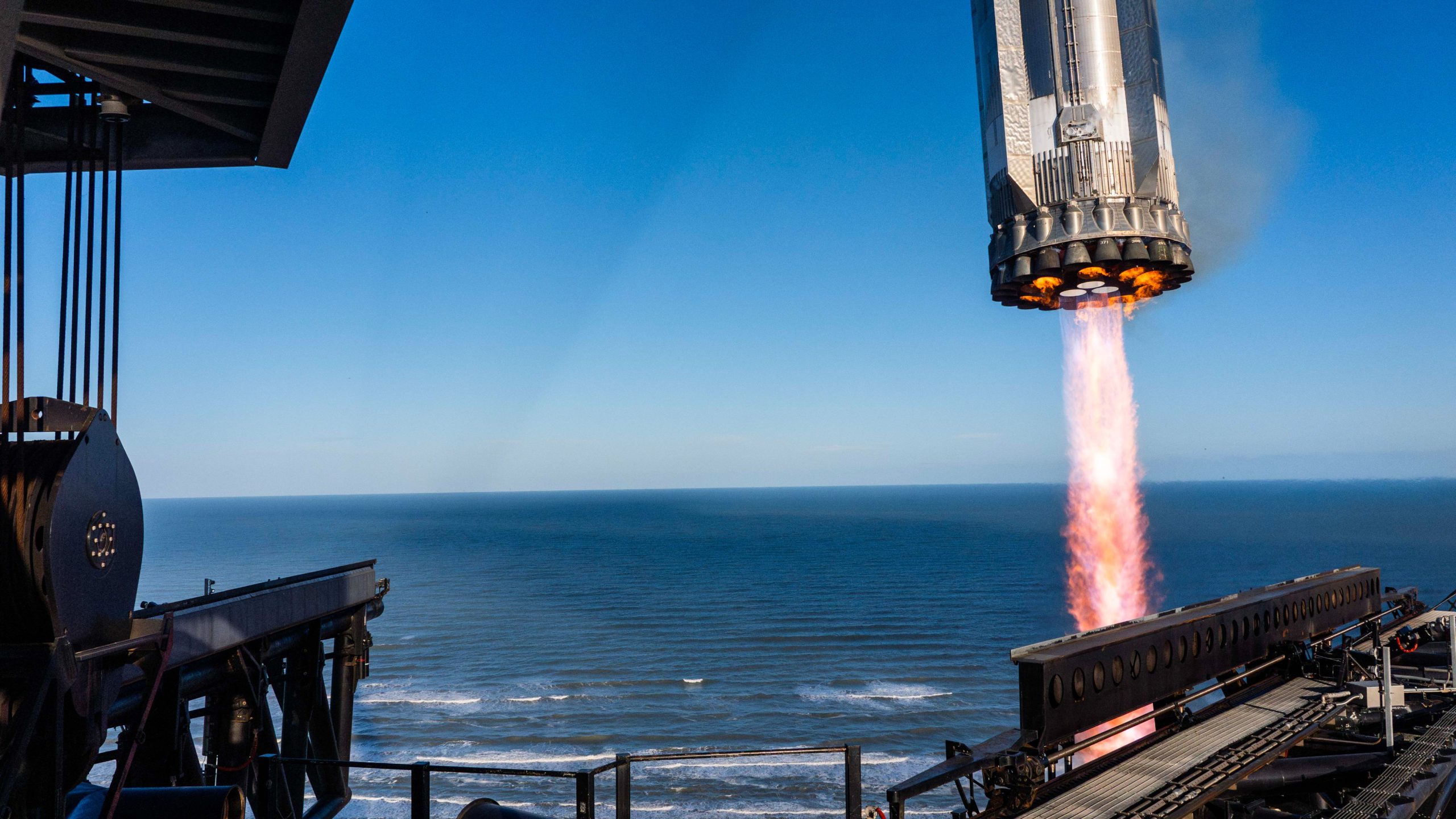

SpaceX and its CEO Elon Musk are starting to shed some light on the potential reasoning for the loss of Starship yesterday, which was lost after a successful launch and catch of the lower-stage booster.
Starship was lost during its ascension, and debris rained down over the Caribbean less than an hour after SpaceX lost all communication with the spacecraft.
A few hours after the launch was over, SpaceX started to shed some light after looking at preliminary data that the rocket left behind.
The company said that a fire developed in the aft section of Starship:
“Following stage separation, the Starship upper stage successfully lit all six Raptor engines and performed its ascent burn to space. Prior to the burn’s completion, telemetry was lost with the vehicle after approximately eight and a half minutes of flight. Initial data indicates a fire developed in the aft section of the ship, leading to a rapid unscheduled disassembly with debris falling into the Atlantic Ocean within the predefined hazard areas.”
Additionally, Musk said that there was some sort of oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall.
The leak was evidently large enough to build more pressure than the vent was able to handle:
🚨Elon Musk has also said an oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could be the cause of the anomaly. https://t.co/BgLkdA9Kk1
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 17, 2025
Some also seemed to recognize evidence of fires throughout the flight of Starship, which is obviously an anomaly:
Unconfirmed but what looks to be fire at the hinge of Starship’s flap. A potential RUD? We await as we get any confirmation from SpaceX.
They do not have comms with the spacecraft as this moment. pic.twitter.com/Cn1EF4AHpv
— Mihir Tripathy (@mihirneal) January 16, 2025
There will be more information regarding the loss of Starship in the coming days and weeks, but Musk already believes that a bit of fire suppression and more volume in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could fix the issue.
“Nothing so far suggests pushing next launch past next month,” he said, so Flight 8 could happen sometime in February.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
SpaceX completes second catch of lower stage, but loses Starship

SpaceX completed its seventh launch of Starship on Thursday, accomplishing a clean liftoff and catch of the first-stage booster. However, the upper stage was lost after its ascent.
The launch took place just a few minutes after 5 p.m. on the East Coast, as the first attempts at getting Starship in the air for the seventh time were delayed by weather both last week and this week.
Conditions were favorable on Thursday as SpaceX looked to follow up a successful campaign by Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos’s company, earlier today.
SpaceX went into the seventh Starship launch with plans for a catch attempt of the first-stage booster, something it attempted and completed during the fifth test launch last year. It decided to skip a catch attempt with the sixth test flight as conditions were not aligned.
For now, SpaceX is extremely selective as to when it attempts catches.
However, it was successful during this attempt, its second completed catch:
🚨 🚀 Here is @SpaceX’s full catch of the Lower Stage Booster from Starship Flight 7! pic.twitter.com/IXIRAGr1Md
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
This flight differed from previous launches as SpaceX rolled out several improvements to the rocket and the processes as it featured plans to do a Starlink deployment simulation and had various adjustments to flap placement and avionics.
These plans were disrupted by the fact that SpaceX lost all communications with Starship about ten minutes into the flight, which the aerospace company confirmed was a result of losing the spacecraft sometime during its ascent.
🚀🚨 Telemetry on Starship has been lost. All comms with the ship have been lost, and SpaceX’s livestream says this is an “anomaly.”
“We are assuming the ship has been lost.” pic.twitter.com/fyyCNuXVRg
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
Although the catch was successful, the loss of the actual rocket seemed to be a huge damper on the entire event. SpaceX confirmed several minutes after the loss of communications that the rocket was destroyed and was lost.
It was its first failure since the second Starship launch in November 2023. SpaceX had no answers for why the rocket was destroyed and lost.
We will keep you updated in the coming days.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
SpaceX confirms next Starship launch target – Here’s when it will take off
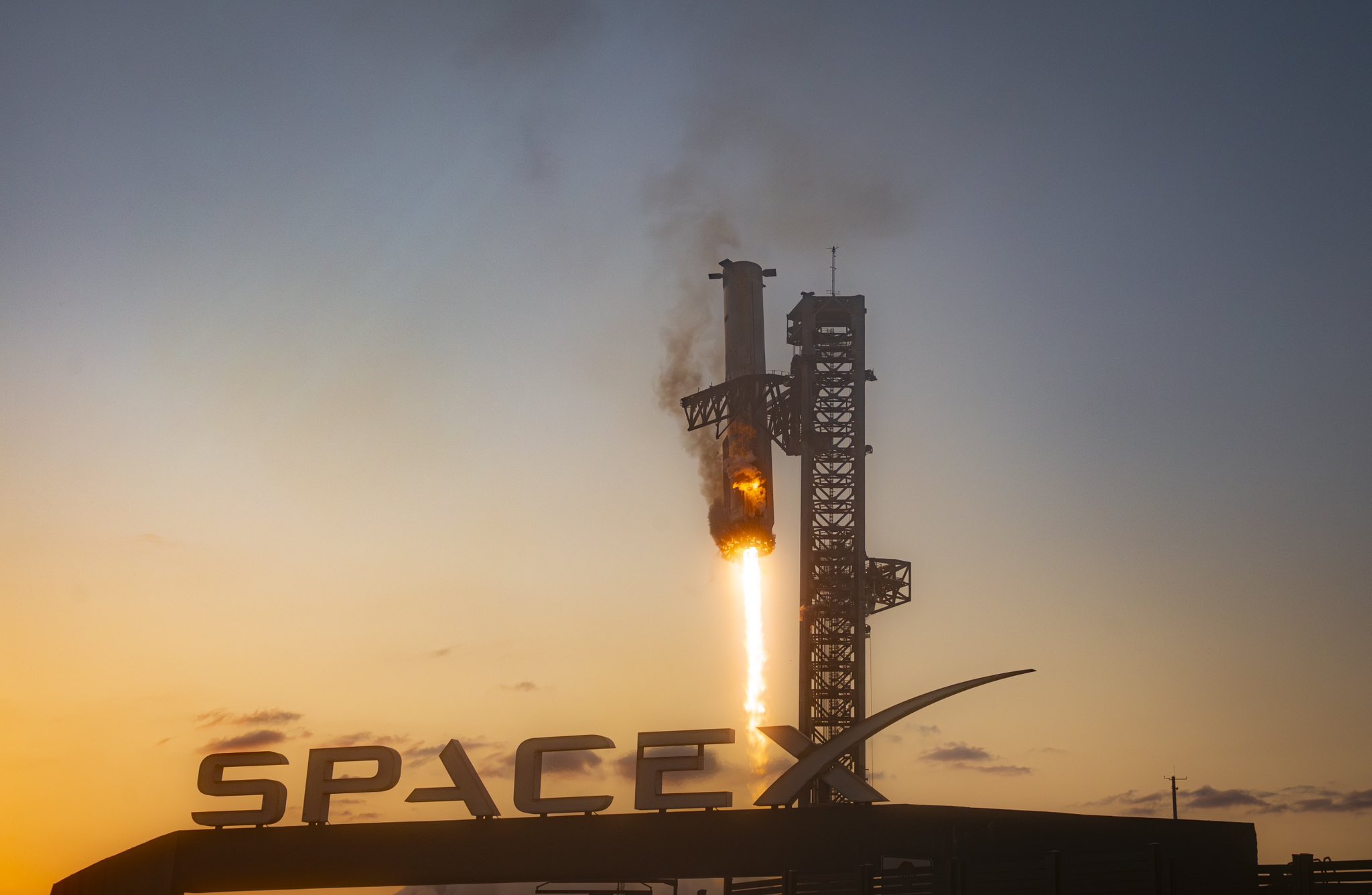

SpaceX has confirmed a new target date for the seventh Starship test launch after weather in Texas delayed the first scheduled date for “three or four days.”
The company is now targeting the launch for Monday, January 13, at 4 p.m. CST or 5 p.m. EST. The launch date is not set in stone as any variety of delays could impact this, but SpaceX hopes to finally take off after a delay that pushed it back from January 10.
🚨 STARSHIP LAUNCH DATE: @SpaceX says Starship’s 7th test flight is now targeted for Monday, January 13 at 4pm CST
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 8, 2025
What’s new with this Starship launch
With this being the seventh test launch of Starship, there are several things that the company will change and hope to accomplish. All of these launches are done in preparation for eventually taking flight to Mars, something that will happen next year, according to CEO Elon Musk.
First, SpaceX is rolling out a next-generation ship with “significant upgrades.” Forward flaps have been made smaller and are repositioned away from the heat shield, which will “reduce their exposure to reentry heating.”
There is also a 25 percent increase in propellant volume, a new fuel feedline system for the Raptor vacuum engines, and a better-than-ever propulsion avionics module that will control the valves and reading sensors.
Avionics, as a whole, underwent a redesign and now have more capability and redundancy for missions as they become more complex.
Starlink test
SpaceX is also planning to deploy 10 Starlink simulators that are similar in size and weight to the next-generation Starlink satellites:
“While in space, Starship will deploy 10 Starlink simulators, similar in size and weight to next-generation Starlink satellites as the first exercise of a satellite deploy mission. The Starlink simulators will be on the same suborbital trajectory as Starship, with splashdown targeted in the Indian Ocean. A relight of a single Raptor engine while in space is also planned.”
Ship return and catch
There will be several experiments that have to do with returning Starship and various catch scenarios and sequences. One of which will see “a significant number of tiles be removed to stress-test vulnerable areas across the vehicle.”
The ship’s reentry profile was also intentionally designed to test the structural limits of the flaps while at the point of maximum dynamic pressure during reentry.
Currently, SpaceX did not detail whether it would attempt another catch during this test launch. These are usually game-time decisions.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.