In emergency medicine, the tools chosen for patient extrication and immobilization are as critical as the medical interventions themselves. One such device, the scoop stretcher, has cemented its importance across pre-hospital and hospital settings, offering specific advantages that can significantly influence patient outcomes. Given the complex dynamics of trauma care—where rapid yet safe movement of patients often dictates survival—the scoop stretcher emerges as a fundamental element in the rescue and stabilization toolkit. Its design, operational advantages, and strategic application make it indispensable, especially in scenarios involving potential spinal injuries, unstable patients, or situations demanding minimal manipulation.
Understanding the Scoop Stretcher: Design, Function, and Use Cases

The scoop stretcher, also known as a spinal or orthopedic stretcher, is a specialized device intended to immobilize and transport patients with suspected spinal injuries, fractures, or other trauma. Its unique construction comprises two hinged, half-length sections that can be assembled around a patient or disassembled for removal with minimal movement. This design allows for a gentle and precise approach to patient handling, reducing the risk of exacerbating spinal injuries—a paramount concern in trauma care.
Structural Characteristics and Operational Mechanics
Constructed typically from lightweight, durable materials such as aluminum alloys or reinforced composites, scoop stretchers prioritize ease of manipulation, strength, and patient safety. The device features adjustable hinge mechanisms, locking systems to maintain stability, and often, ergonomic handles for controlled lifting and transfer. When in use, rescue personnel can slide the device under the patient, secure the halves around the torso, and then lift or transport the individual as needed. The process minimizes movement of the cervical spine, which is critical in possible spinal injury cases.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Weight | Typically ranges from 5 to 8 pounds, facilitating ease of transport by a team of responders |
| Length Adjustment | Ranged from 6 to 8 feet, accommodating adult to pediatric patients through telescoping or segmented designs |
| Material Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio materials deliver superior load capacity (~1000 pounds) while keeping the device portable |
Core Benefits of Using a Scoop Stretcher in Emergency Situations
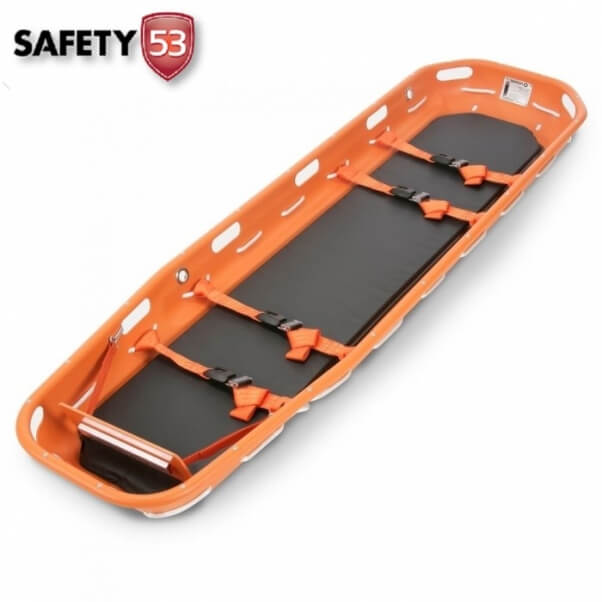

The deployment of a scoop stretcher offers multiple advantages that are rooted in its design, operational versatility, and clinical outcomes. These benefits influence pre-hospital interventions, rapid extrication, and definitive care procedures, making it a preferred tool for emergency responders worldwide.
1. Minimization of Spinal and Musculoskeletal Injury Risks
Perhaps the most compelling advantage of the scoop stretcher is its capacity to facilitate spinal immobilization and securement with minimal movement. In trauma scenarios—such as vehicular collisions, falls from height, or sporting accidents—the risk of aggravating cervical or back injuries can be life-threatening. The scoop stretcher’s ability to encase the patient, combined with immobilization devices like cervical collars, reduces the likelihood of secondary injury.
2. Enhanced Patient Safety and Comfort During Extrication
The symmetrical construction around the patient allows for uniform support, decreasing discomfort and anxiety. Additionally, the gentle handling reduces pain, especially in fractures or dislocations, and promotes a more dignified rescue experience. The design is conducive to quick, controlled lifting and transfer, which is essential when time is of the essence.
3. Accessibility to Difficult or Confined Environments
Unique to scoop stretchers is their modular assembly. They can be placed around a patient in confined spaces—such as vehicle interiors, narrow stairwells, or rugged terrains—where traditional stretchers cannot maneuver easily. This adaptability accelerates the extrication process, crucial in time-sensitive emergencies like cardiac arrest or airway compromise.
4. Compatibility with Pre-Hospital and Hospital Protocols
Given their widespread acceptance in advanced trauma life support (ATLS) protocols, scoop stretchers integrate seamlessly into established frameworks. They facilitate smooth transition from rescue to definitive hospital care, as they can be stabilized around the patient prior to transfer onto other immobilization devices or stretchers used during ambulance transport or hospital imaging.
5. Facilitating Multidisciplinary and Interagency Collaboration
In multi-agency responses—such as police, fire department, and emergency medical services—the scoop stretcher’s straightforward assembly and operation promote efficient teamwork. Clear, standardized procedures support smoother coordination, reducing response times and improving overall patient management in complex scenarios.
Operational Best Practices and Technical Considerations
To maximize the benefits of scoop stretchers, responders must adhere to specific operational guidelines. These include proper patient assessment, immobilization in accordance with trauma protocols, and safe handling during transfer. Correct application, maintenance, and regular training are vital to preserve device integrity and ensure proficiency among responders.
Proper Assembly and Application Procedure
Rescue personnel should initially evaluate the scene, ensuring stabilization of the patient’s neck and spine if spinal injury is suspected. The scoop stretcher's halves are then gently aligned and assembled around the patient, ensuring minimal movement of the neck. Candidates for immobilization must have the head secured with cervical collars, and the device should be locked securely prior to lifting. Lifting is performed with coordinated effort, maintaining spinal alignment throughout.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular checks for structural integrity, hinge function, locking mechanisms, and cleanliness are critical. Damaged or worn components compromise safety and should be replaced or serviced promptly. Ensuring the device is free of corrosion and debris enhances longevity and operational efficiency.
Training and Skill Development
Ongoing simulation-based training ensures that responders are familiar with assembly, patient handling, and emergency deployment. Familiarity with various environmental adaptations—such as uneven terrain or confined spaces—further enhances responder confidence and patient safety.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Training Frequency | Recommended quarterly for first responders, with annual refresher courses |
| Inspection Checklist | Hinge operation, locking system, structural integrity, and cleanliness |
Limitations and Challenges in Using a Scoop Stretcher
While the scoop stretcher offers notable advantages, it is not without limitations. Understanding these challenges is necessary to optimize its use and avoid misconceptions that could impede patient care.
1. Size and Weight Constraints
Although lightweight, scoop stretchers may still be cumbersome in certain environments, particularly in very tight or unstable settings. Their size might restrict maneuverability in confined spaces or when rapid deployment is needed in multi-patient scenarios.
2. Potential for Improper Application
Incorrect assembly or failure to secure the device properly can lead to increased movement of the patient or device failure during transfer. Such errors underscore the significance of comprehensive training and adherence to procedural standards.
3. Limitations with Certain Patient Populations
Extremely obese patients or those with complex injuries may require alternative immobilization strategies. Additionally, pediatric patients sometimes necessitate specialized adaptations or devices designed specifically for their size and fragility.
4. Dependence on Skilled Personnel
The effectiveness of scoop stretchers hinges on the responders' proficiency. Inexperienced personnel might inadvertently cause additional injury through improper handling or application errors.
Future Directions and Innovations

Advancements in materials science, ergonomic design, and portable modular systems promise to enhance the functionality of scoop stretchers further. Concepts such as collapsible models, integrated stabilization features, and smart devices equipped with sensors for real-time feedback are on the horizon, potentially revolutionizing trauma immobilization protocols.
Emerging Technologies and Their Potential Impact
Innovations like lightweight composites equipped with embedded accelerometers or tension sensors could allow responders to monitor proper immobilization dynamically. Additionally, compatibility with other rescue equipment, such as extrication tools and patient monitoring systems, would streamline multi-modal rescue strategies.
| Relevant Category | Projected Developments |
|---|---|
| Material Technology | Use of ultra-light, durable composites for easier handling and increased load capacity |
| Integration | Smart sensors for quality assurance and real-time feedback during application |
| Design Innovation | Foldable, modular units enabling easier transport and storage in emergency kits |
Conclusion: Strategically Employing Scoop Stretchers for Optimal Trauma Care
The scoop stretcher stands out as an essential device that bridges the gap between rapid extracation and safe immobilization in trauma care. Its ability to reduce secondary injury risk, facilitate accessibility, and enhance team coordination underpins its central role in modern emergency response. The ongoing refinement of design, training, and integration with emerging technologies will undoubtedly solidify its position as a cornerstone of pre-hospital trauma management well into the future.
How does a scoop stretcher differ from traditional stretchers?
+The scoop stretcher is designed to assemble around a patient, allowing for minimal movement—particularly of the spine—making it ideal for trauma cases. Traditional stretchers are typically rigid and require the patient to be moved onto them, which can pose risks if spinal injuries are present.
What training is necessary for responders to effectively use a scoop stretcher?
+Proper training involves understanding assembly procedures, immobilization techniques, patient handling, and environmental adaptations. Regular simulation exercises and maintenance checks are recommended to maintain proficiency and ensure safety.
Are scoop stretchers suitable for pediatric trauma patients?
+Yes, but pediatric-specific scoop stretchers or adapters are advisable to accommodate smaller sizes safely and reliably. Proper immobilization is especially vital given the fragility of pediatric patients.
What are common pitfalls in using scoop stretchers?
Common pitfalls include improper assembly, inadequate securing of the device, and insufficient immobilization. These errors can lead to secondary injuries or device failure—highlighting the importance of rigorous training and adherence to protocols.

