The preterite tense in Spanish is a fundamental concept for any language learner, as it allows speakers to describe completed actions that occurred in the past. Mastering the preterite conjugations is essential to convey past events effectively and accurately. In this article, we will delve into the world of preterite Spanish conjugations, exploring the regular and irregular patterns, and providing examples to illustrate their usage.
Introduction to Preterite Conjugations
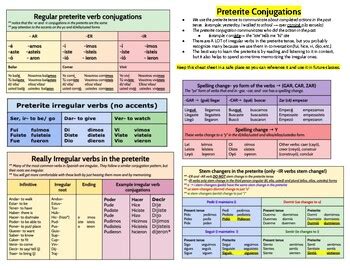
The preterite tense is used to describe actions that started and finished in the past, and it is often translated to English as the simple past tense. The conjugation of verbs in the preterite tense depends on the verb’s ending, which can be -ar, -er, or -ir. Each verb type has its own set of conjugation rules, which we will examine in detail.
Key Points
- The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past.
- Regular -ar verbs follow a specific conjugation pattern.
- Regular -er and -ir verbs have distinct conjugation patterns.
- Irregular verbs do not follow the standard conjugation rules.
- Preterite conjugations are essential for effective communication in Spanish.
Regular -ar Verb Conjugations
Regular -ar verbs are the most common type of verb in Spanish, and they follow a predictable conjugation pattern in the preterite tense. The conjugation of a regular -ar verb is formed by adding the following endings to the verb stem: -é, -aste, -ó, -amos, -asteis, and -aron. For example, the verb “hablar” (to speak) is conjugated as follows:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | hablé |
| Tú | hablaste |
| Él/ella/usted | habló |
| Nosotros/as | hablamos |
| Vosotros/as | hablasteis |
| Ellos/as | hablaron |
Regular -er and -ir Verb Conjugations
Regular -er and -ir verbs also follow a specific conjugation pattern in the preterite tense. The conjugation of a regular -er verb is formed by adding the following endings to the verb stem: -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron. For example, the verb “comer” (to eat) is conjugated as follows:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | comí |
| Tú | comiste |
| Él/ella/usted | comió |
| Nosotros/as | comimos |
| Vosotros/as | comisteis |
| Ellos/as | comieron |
Regular -ir verbs follow a similar pattern, with the following endings: -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron. For example, the verb "vivir" (to live) is conjugated as follows:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | viví |
| Tú | viviste |
| Él/ella/usted | vivió |
| Nosotros/as | vivimos |
| Vosotros/as | vivisteis |
| Ellos/as | vivieron |
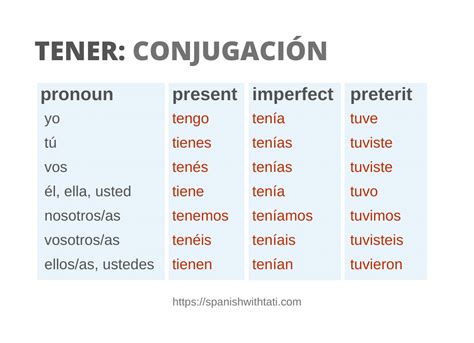
Irregular Verb Conjugations

Irregular verbs in Spanish do not follow the standard conjugation rules and must be memorized separately. Some common irregular verbs in the preterite tense include “ser” (to be), “estar” (to be), “tener” (to have), and “ir” (to go). For example, the verb “ser” is conjugated as follows:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | fui |
| Tú | fuiste |
| Él/ella/usted | fue |
| Nosotros/as | fuimos |
| Vosotros/as | fuisteis |
| Ellos/as | fueron |
Preterite Conjugations in Context
Understanding the preterite conjugations is crucial for effective communication in Spanish. By mastering the conjugation patterns, you can describe past events with accuracy and clarity. For example:
Yo hablé con mi amigo ayer. (I spoke with my friend yesterday.)
Él comió una manzana esta mañana. (He ate an apple this morning.)
Nosotros vivimos en Madrid durante cinco años. (We lived in Madrid for five years.)
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the preterite conjugations is a fundamental step in becoming proficient in Spanish. By understanding the regular and irregular conjugation patterns, you can effectively communicate past events and improve your overall language skills. Remember to practice the conjugations regularly and use them in context to reinforce your learning.
What is the preterite tense used for in Spanish?
+The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions that occurred in the past.
How do I conjugate regular -ar verbs in the preterite tense?
+Regular -ar verbs are conjugated by adding the following endings to the verb stem: -é, -aste, -ó, -amos, -asteis, and -aron.
What are some common irregular verbs in the preterite tense?
+Some common irregular verbs in the preterite tense include “ser”, “estar”, “tener”, and “ir”.

