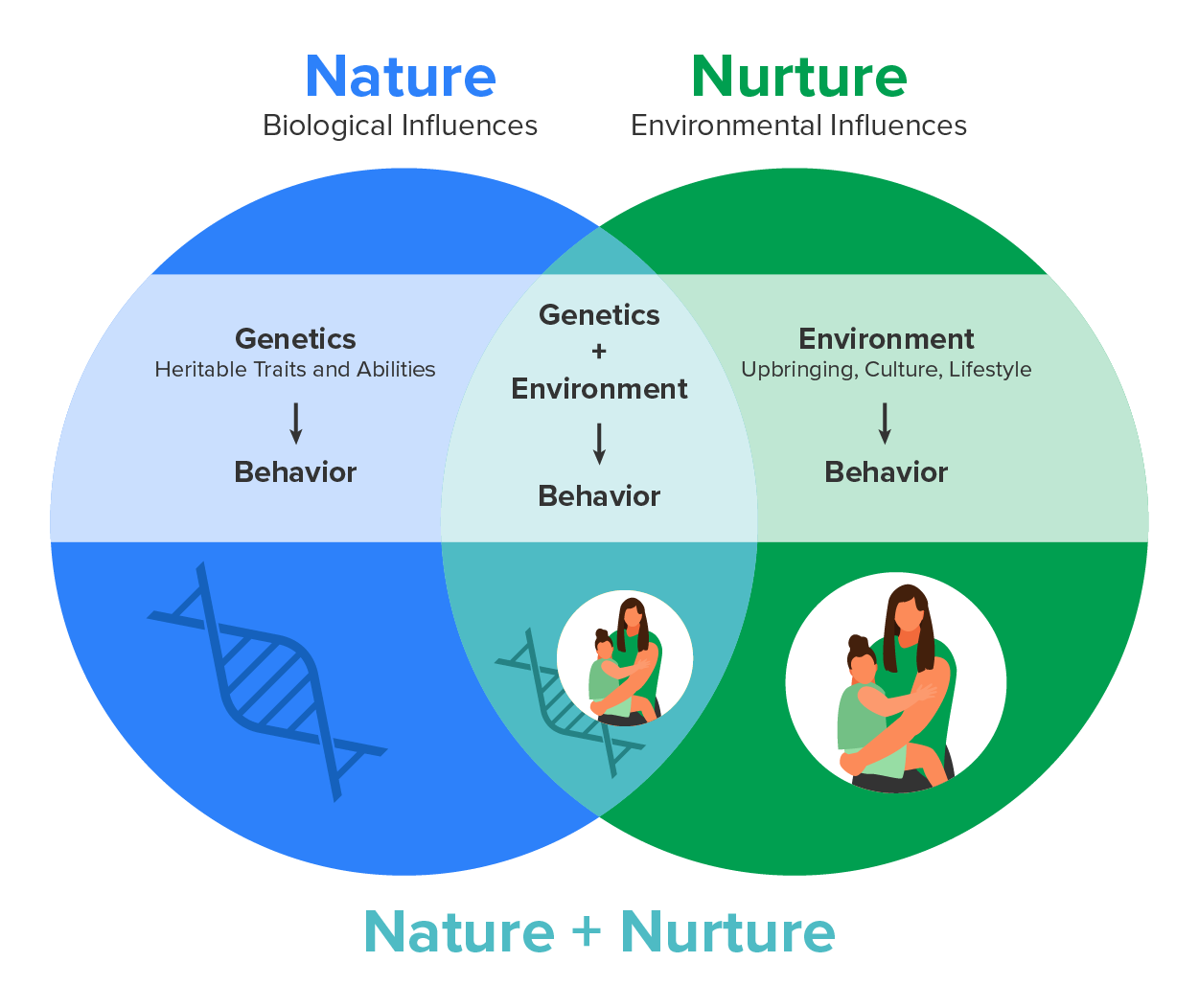
The nature vs nurture debate has been a longstanding and contentious issue in the fields of psychology, philosophy, and biology. At its core, the debate revolves around the question of whether human behavior, personality, and intelligence are primarily influenced by genetic factors (nature) or by environmental factors (nurture). This dichotomy has been a subject of discussion and research for centuries, with each side presenting compelling arguments and evidence.
The nature perspective posits that human traits and behaviors are largely determined by genetics, with heredity playing a significant role in shaping who we are and how we behave. Proponents of this view argue that genetic differences account for variations in intelligence, personality, and behavior among individuals. They point to studies on twins and adoptees, which have shown significant similarities in behavior and traits between genetically related individuals, even when they are raised in different environments. For instance, a study on identical twins raised apart found that they shared similar personality traits, interests, and even mannerisms, despite being separated at birth.
On the other hand, the nurture perspective suggests that human behavior and traits are primarily shaped by environmental factors, such as upbringing, culture, and life experiences. Advocates of this view argue that our genes provide a foundation, but it is the environment that ultimately determines how we develop and behave. They point to the fact that identical twins can exhibit different behaviors and traits when raised in different environments, and that adoption studies have shown that children can develop traits and behaviors similar to those of their adoptive parents. For example, a study on language development found that children adopted by families speaking a different language can quickly adapt and develop fluency in the new language, despite having no prior exposure to it.
Key Points
- The nature vs nurture debate revolves around the question of whether human behavior and traits are primarily influenced by genetics or environment.
- Studies on twins and adoptees have shown significant similarities in behavior and traits between genetically related individuals.
- Environmental factors, such as upbringing and culture, play a significant role in shaping human behavior and traits.
- Identical twins can exhibit different behaviors and traits when raised in different environments.
- Adoption studies have shown that children can develop traits and behaviors similar to those of their adoptive parents.
Genetic Factors and Heritability
Genetic factors play a significant role in shaping human behavior and traits. Heritability estimates, which quantify the proportion of variation in a trait that can be attributed to genetic differences, have been found to be significant for many traits, including intelligence, personality, and behavior. For example, a meta-analysis of twin and adoption studies found that the heritability of intelligence quotient (IQ) is around 50-60%, indicating that genetic differences account for approximately half of the variation in IQ among individuals.
However, it is essential to note that heritability estimates are often misinterpreted as implying that genetics determine the majority of the variation in a trait. In reality, heritability estimates only provide information about the relative contribution of genetic and environmental factors to the variation in a trait, and do not imply that genetics is the sole or primary cause of the trait. Additionally, heritability estimates can vary depending on the population being studied and the specific trait being examined.
Epigenetics and Gene-Environment Interactions
Recent advances in epigenetics have highlighted the complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, can influence gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. These modifications can be influenced by environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or stress, and can have a significant impact on behavior and traits. For example, a study on maternal care found that rats that received high levels of maternal care had altered epigenetic marks on genes involved in stress response, which was associated with improved behavioral outcomes.Furthermore, gene-environment interactions can also influence the expression of genetic traits. For instance, a genetic predisposition to a particular trait may only be expressed in certain environmental contexts. This highlights the importance of considering the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in understanding human behavior and traits.
| Trait | Heritability Estimate |
|---|---|
| Intelligence Quotient (IQ) | 50-60% |
| Personality Traits | 30-50% |
| Behavioral Traits | 20-40% |
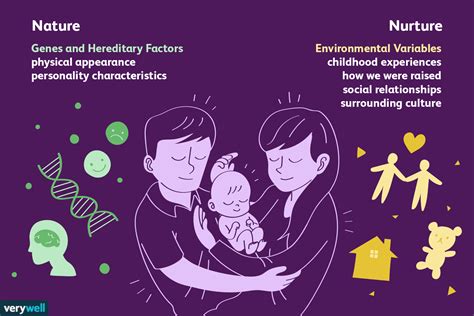
Environmental Factors and Development

Environmental factors, such as upbringing, culture, and life experiences, play a significant role in shaping human behavior and traits. For example, a child raised in a supportive and nurturing environment is more likely to develop positive behavioral traits, such as empathy and self-esteem, compared to a child raised in a neglectful or abusive environment. Additionally, cultural and socioeconomic factors can influence access to resources, education, and healthcare, which can have a significant impact on behavioral and psychological outcomes.
Furthermore, life experiences, such as trauma or stress, can also shape behavior and traits. For instance, a person who experiences chronic stress may develop anxiety or depression, while a person who experiences trauma may develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Understanding the impact of environmental factors on behavior and traits is essential for developing effective interventions and treatments.
Neuroplasticity and Brain Development
Recent advances in neuroplasticity have highlighted the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt in response to environmental factors. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to rewire and adapt throughout life, in response to new experiences, learning, and environmental factors. For example, a study on London taxi drivers found that the hippocampus, a region involved in spatial memory, was larger in drivers who had to memorize complex maps and navigate through the city.Furthermore, brain development is also influenced by environmental factors, such as nutrition, sleep, and exercise. For instance, a study on the effects of maternal nutrition on fetal brain development found that mothers who consumed a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids had children with improved cognitive outcomes.
What is the current consensus on the nature vs nurture debate?
+The current consensus is that both genetic and environmental factors contribute to human behavior and traits, and that the interplay between the two is complex and bidirectional.
How do epigenetic modifications influence gene expression?
+Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, can influence gene expression by altering the accessibility of genes to transcription factors and other regulatory proteins.
What is the role of neuroplasticity in brain development and function?
+Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to rewire and adapt throughout life, in response to new experiences, learning, and environmental factors, and plays a critical role in brain development and function.
In conclusion, the nature vs nurture debate is a complex and multifaceted issue that has been a subject of discussion and research for centuries. While both genetic and environmental factors contribute to human behavior and traits, the interplay between the two is complex and bidirectional. Understanding the relative contributions of each factor is crucial for developing effective interventions and treatments for various behavioral and psychological disorders. By considering the complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors, we can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms that shape human behavior and traits.