The medial vastus muscle, also known as the vastus medialis, is a crucial component of the quadriceps femoris muscle group in the thigh. It plays a significant role in knee extension, stabilization, and overall lower limb function. As one of the four quadriceps muscles, the medial vastus muscle works in concert with the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, and vastus intermedius to facilitate movements such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Located on the medial (inner) aspect of the thigh, the medial vastus muscle originates from the medial aspect of the femur (thigh bone) and inserts into the patella (kneecap) via the quadriceps tendon. This tendon then continues as the patellar ligament, attaching to the tibial tuberosity on the anterior (front) surface of the tibia (shin bone). The medial vastus muscle's unique anatomy, with its oblique fibers, enables it to contribute to both knee extension and medial (internal) rotation of the tibia.
Key Points
- The medial vastus muscle is part of the quadriceps femoris muscle group, crucial for knee extension and lower limb function.
- It originates from the medial aspect of the femur and inserts into the patella, contributing to knee stability and movement.
- The muscle's oblique fibers facilitate both knee extension and medial rotation of the tibia.
- Weakness or imbalance in the medial vastus muscle can lead to issues such as patellofemoral pain syndrome and knee instability.
- Strengthening exercises, such as squats and lunges, can help improve medial vastus muscle function and overall knee health.
Function and Importance of the Medial Vastus Muscle
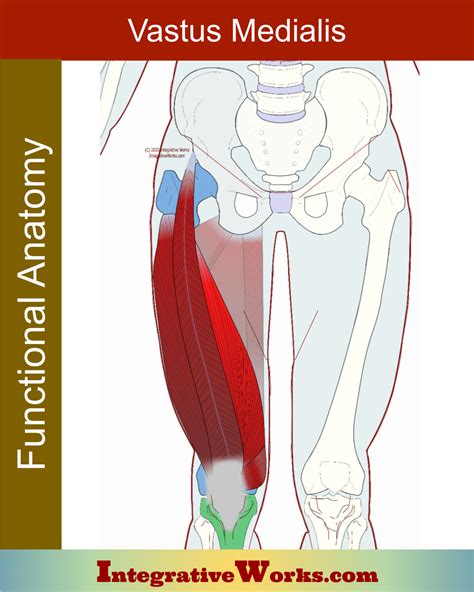
The medial vastus muscle’s primary function is to extend the knee joint, which is essential for activities that involve straightening the knee, such as standing up from a seated position or kicking a ball. Additionally, it helps to stabilize the patella and maintain proper tracking of the knee joint, ensuring smooth movement and reducing the risk of injury. The muscle’s medial rotation component also assists in correcting the rotation of the tibia during the late stages of knee extension, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of lower limb movement.
Biomechanical Considerations and Clinical Relevance
From a biomechanical perspective, the medial vastus muscle plays a critical role in maintaining the health and integrity of the knee joint. Weakness or imbalance in this muscle can lead to various issues, including patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), characterized by pain around or behind the patella, and knee instability, which can increase the risk of falls and further injury. Furthermore, studies have shown that strengthening the medial vastus muscle, along with other components of the quadriceps, can help alleviate symptoms of PFPS and improve overall knee function.
| Muscle Component | Function | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Medial Vastus | Knee Extension, Medial Rotation | PFPS, Knee Instability |
| Rectus Femoris | Knee Extension, Hip Flexion | Hamstring Strains, Hip Flexor Injuries |
| Vastus Lateralis | Knee Extension, Lateral Rotation | IT Band Syndrome, Lateral Knee Pain |

Training and Rehabilitation Strategies

Given the medial vastus muscle’s importance in knee function and overall lower limb movement, incorporating exercises that target this muscle into training and rehabilitation programs is essential. Squats, lunges, and leg press exercises are effective for strengthening the quadriceps, including the medial vastus. Additionally, specific exercises such as the terminal knee extension (TKE) exercise, which isolates the last 10-15 degrees of knee extension, can be particularly beneficial for targeting the medial vastus muscle.
For individuals with knee injuries or pathologies, a comprehensive rehabilitation program should include exercises that strengthen the medial vastus muscle in conjunction with other muscle groups around the knee, such as the hamstrings and hip stabilizers. This balanced approach helps ensure proper knee mechanics, reduces the risk of further injury, and promotes optimal recovery and functional return.
Future Directions and Research
Future research should continue to explore the role of the medial vastus muscle in knee function and pathology, with a focus on developing more effective training and rehabilitation strategies. The integration of advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and ultrasound, can provide valuable insights into muscle morphology and function, helping to inform the development of personalized exercise programs. Furthermore, the exploration of neuromuscular training methods, which aim to enhance the neural drive to the muscle, may offer additional benefits in terms of improving muscle function and reducing injury risk.
What is the primary function of the medial vastus muscle?
+The primary function of the medial vastus muscle is to extend the knee joint and contribute to medial rotation of the tibia, playing a crucial role in lower limb movement and knee stability.
How can weakness in the medial vastus muscle affect knee health?
+Weakness in the medial vastus muscle can lead to issues such as patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) and knee instability, increasing the risk of injury and compromising overall knee function.
What exercises are effective for strengthening the medial vastus muscle?
+Exercises such as squats, lunges, and the terminal knee extension (TKE) exercise are effective for strengthening the medial vastus muscle. A comprehensive training program should also include exercises that target other muscle groups around the knee to ensure balanced strength and optimal knee function.