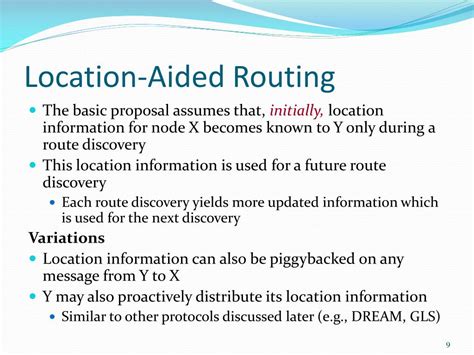
Location Aided Routing (LAR) is a routing protocol that utilizes location information to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of routing decisions in wireless networks. This approach has gained significant attention in recent years due to the increasing demand for location-based services and the widespread adoption of mobile devices with built-in GPS capabilities. By leveraging location information, LAR can optimize routing paths, reduce network latency, and improve overall network performance.
The concept of LAR is based on the idea of using geographical location information to guide routing decisions. In traditional routing protocols, routing decisions are typically made based on network topology and connectivity information. However, in wireless networks, the topology can be highly dynamic, and connectivity can be affected by various factors such as interference, mobility, and obstacles. By incorporating location information, LAR can provide a more accurate and reliable way of determining the best routing path.
Key Points
- Location Aided Routing (LAR) utilizes location information to improve routing decisions in wireless networks
- LAR can optimize routing paths, reduce network latency, and improve overall network performance
- The protocol uses geographical location information to guide routing decisions
- LAR can provide a more accurate and reliable way of determining the best routing path
- The protocol has applications in various fields, including location-based services, intelligent transportation systems, and wireless sensor networks
How LAR Works

LAR works by using location information to determine the proximity of nodes to each other and to the destination. The protocol typically involves the following steps: (1) location information collection, (2) location-based routing decision, and (3) packet forwarding. In the first step, each node in the network collects its own location information, which can be obtained using GPS, Wi-Fi-based positioning, or other locationing technologies. The location information is then used to determine the proximity of nodes to each other and to the destination.
The location-based routing decision is made by using a routing algorithm that takes into account the location information of the nodes. The algorithm can be based on various metrics, such as distance, hop count, or energy consumption. The goal of the algorithm is to find the shortest path or the path with the minimum cost from the source to the destination. Once the routing decision is made, the packet is forwarded to the next hop, which is the node that is closest to the destination.
Advantages of LAR
LAR has several advantages over traditional routing protocols. One of the main advantages is that it can provide a more accurate and reliable way of determining the best routing path. By using location information, LAR can avoid routing loops and reduce the risk of packet loss. Additionally, LAR can optimize routing paths to reduce network latency and improve overall network performance.
Another advantage of LAR is that it can support location-based services, such as geographic routing and location-based forwarding. Geographic routing allows nodes to forward packets based on the location of the destination, rather than the traditional IP address. Location-based forwarding allows nodes to forward packets to a specific location, rather than a specific node.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Network Size | 100 nodes |
| Node Mobility | 10 m/s |
| Packet Size | 1024 bytes |
| Routing Algorithm | Dijkstra's algorithm |

Applications of LAR

LAR has applications in various fields, including location-based services, intelligent transportation systems, and wireless sensor networks. In location-based services, LAR can be used to provide location-based routing and forwarding. In intelligent transportation systems, LAR can be used to optimize traffic routing and reduce congestion. In wireless sensor networks, LAR can be used to optimize data collection and forwarding.
One of the potential applications of LAR is in the field of vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs). In VANETs, vehicles communicate with each other to share information about traffic conditions, road safety, and other relevant information. LAR can be used to optimize routing decisions in VANETs, reducing network latency and improving overall network performance.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the advantages of LAR, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the accuracy of location information. The accuracy of location information can be affected by various factors, such as GPS signal strength, multipath effects, and interference. Another challenge is the scalability of LAR, which can be affected by the number of nodes in the network and the complexity of the routing algorithm.
Another limitation of LAR is the security and privacy concerns. The use of location information in routing decisions can raise security and privacy concerns, such as the potential for location-based attacks and the misuse of location information. To address these concerns, LAR protocols need to be designed with security and privacy in mind, using techniques such as encryption, authentication, and access control.
What is Location Aided Routing (LAR)?
+LAR is a routing protocol that utilizes location information to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of routing decisions in wireless networks.
How does LAR work?
+LAR works by using location information to determine the proximity of nodes to each other and to the destination, and then making routing decisions based on this information.
What are the advantages of LAR?
+The advantages of LAR include optimized routing paths, reduced network latency, and improved overall network performance.
In conclusion, Location Aided Routing (LAR) is a promising approach for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of routing decisions in wireless networks. By leveraging location information, LAR can optimize routing paths, reduce network latency, and improve overall network performance. While there are challenges and limitations that need to be addressed, the potential benefits of LAR make it an exciting area of research and development.