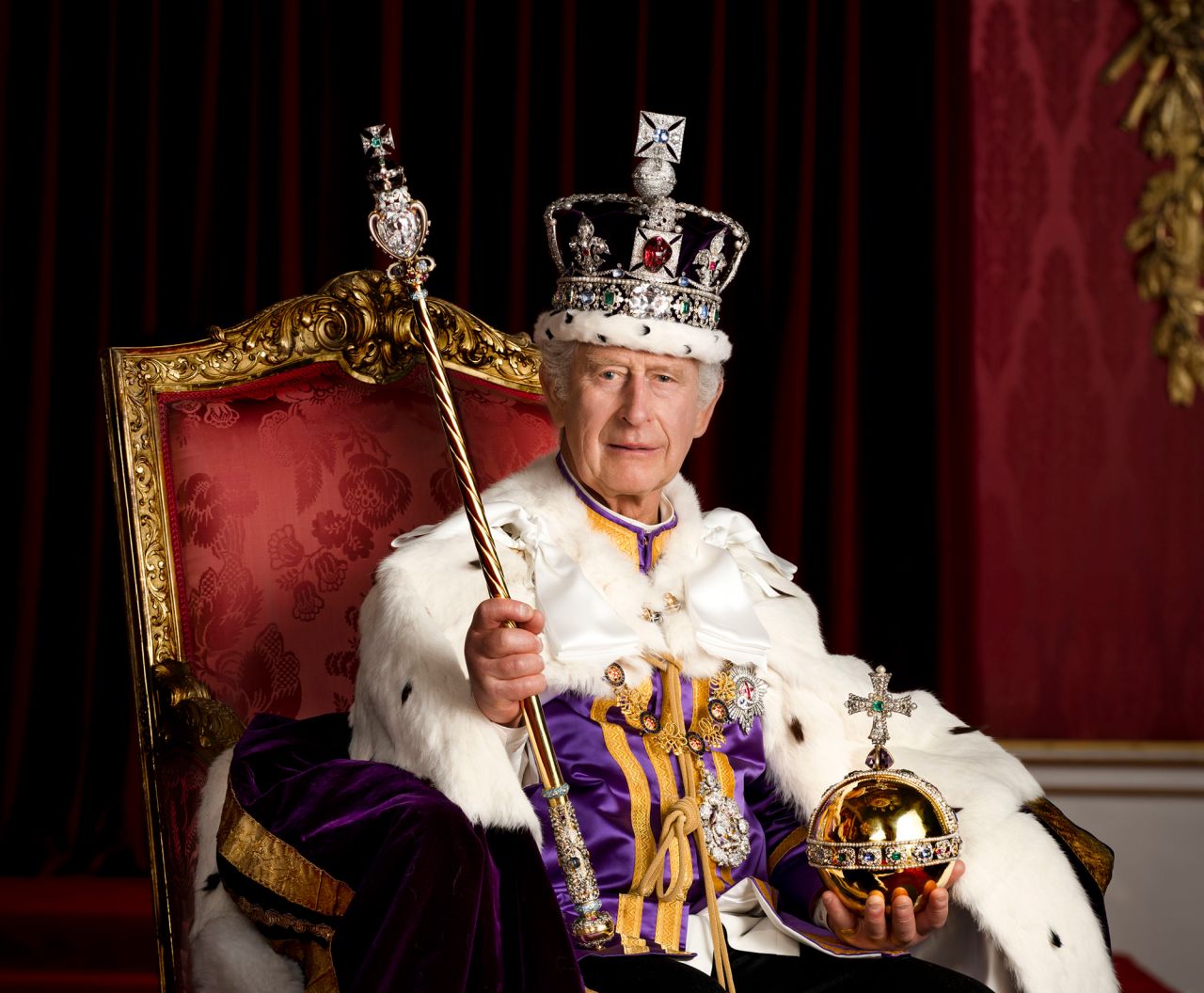
The concept of a king next in line to the throne is a centuries-old tradition that has been a cornerstone of monarchies around the world. The idea of a clear line of succession is crucial in maintaining stability and continuity in a monarchical system of government. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of royal succession, exploring the historical context, the rules that govern it, and the current state of monarchies around the world.
Historical Context of Royal Succession
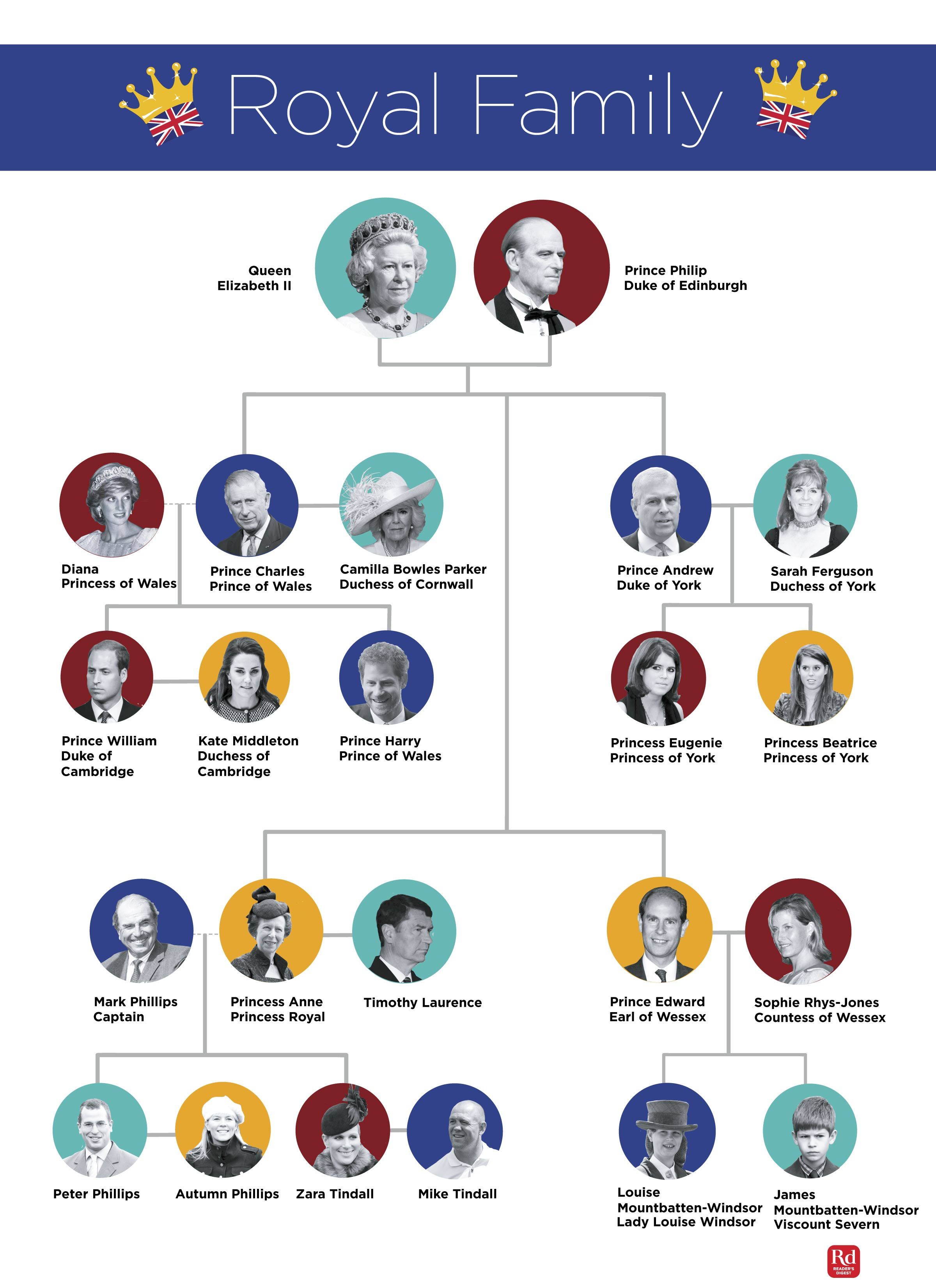
Royal succession has its roots in the medieval period, where the concept of primogeniture, or the right of the firstborn to inherit the throne, was first introduced. This system was designed to prevent disputes and ensure a smooth transition of power. Over time, the rules of succession have evolved, with many monarchies adopting more complex systems that take into account factors such as gender, marriage, and legitimacy. For instance, the Act of Settlement of 1701 in England established that the throne must pass to the monarch’s closest Protestant relative, while the Salic Law in France prohibited women from inheriting the throne.
Rules of Succession
The rules of succession vary from one monarchy to another, but most follow a similar pattern. In general, the monarch’s children and siblings are the first in line to the throne, followed by more distant relatives. In some monarchies, such as the British monarchy, the rules of succession are governed by a combination of statute law and common law. The Succession to the Crown Act of 2013, for example, removed the disqualification of individuals who marry a Roman Catholic, while the Bill of Rights of 1689 established the principle of parliamentary supremacy.
| Monarchy | Rules of Succession |
|---|---|
| British Monarchy | Primogeniture, with the monarch's children and siblings first in line |
| Spanish Monarchy | Primogeniture, with the monarch's children and siblings first in line, and a preference for males over females |
| Saudi Monarchy | Agnatic seniority, with the monarch's brothers and cousins first in line |

Current State of Monarchies
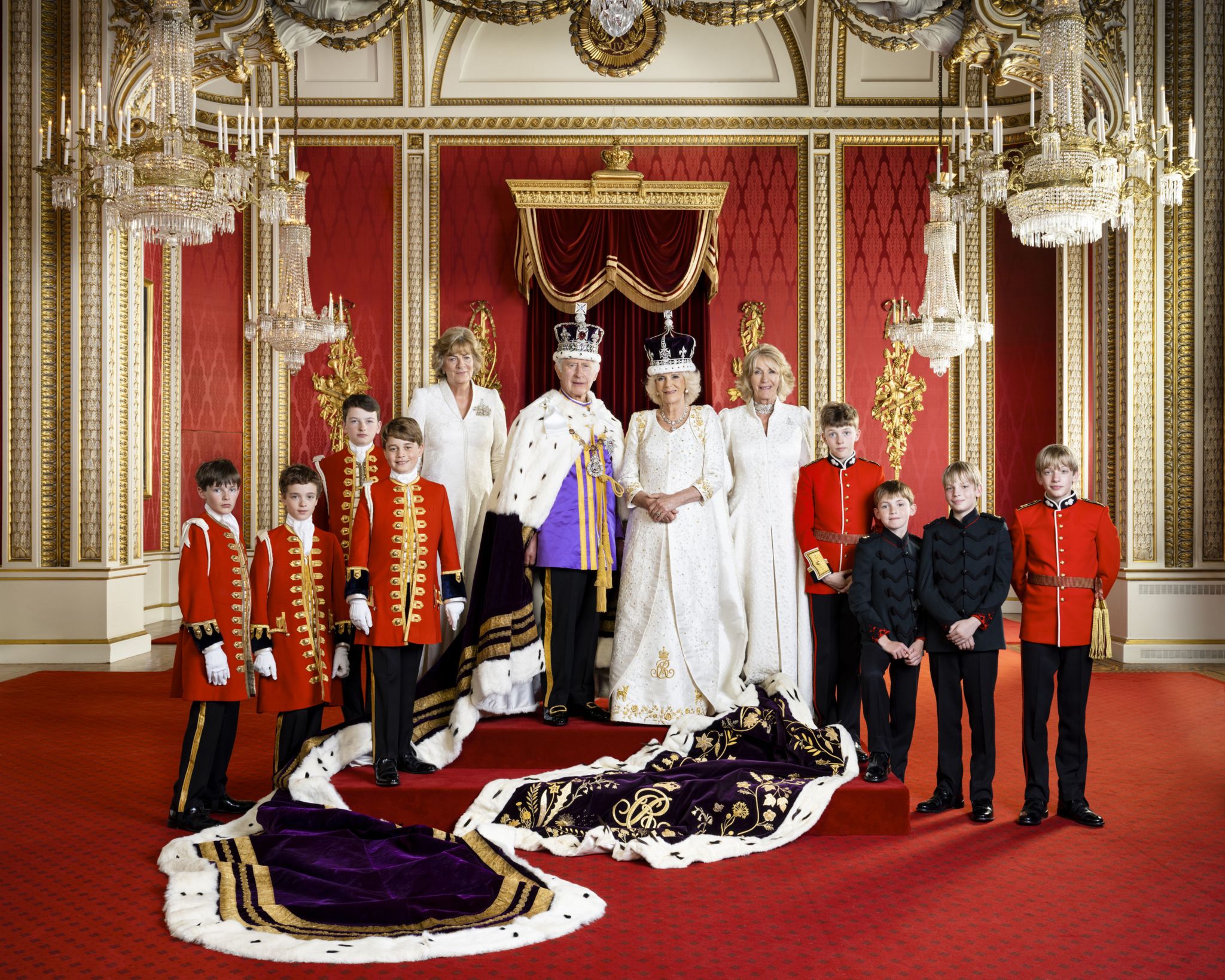

Today, there are 43 monarchies around the world, with the majority located in Europe and the Middle East. The British monarchy is one of the most well-known and respected monarchies, with a history dating back over 1,000 years. Other notable monarchies include the Saudi monarchy, the Jordanian monarchy, and the Japanese monarchy. According to a survey conducted by the Pew Research Center, 71% of people in the United Kingdom believe that the monarchy is an important part of the country’s identity, while 64% of people in Saudi Arabia believe that the monarchy is essential to the country’s stability.
Challenges Facing Monarchies
Despite their rich history and cultural significance, monarchies face a number of challenges in the modern era. One of the biggest challenges is the need to adapt to changing social and political norms. Many monarchies have had to evolve to accommodate changes such as the end of absolute monarchy and the introduction of democratic reforms. For example, the Spanish monarchy has implemented various reforms, including the establishment of a constitutional monarchy and the recognition of the rights of women and minorities.
Key Points
- The concept of a king next in line to the throne is a centuries-old tradition that has been a cornerstone of monarchies around the world.
- The rules of succession vary from one monarchy to another, but most follow a similar pattern, with the monarch's children and siblings first in line.
- Monarchies face a number of challenges in the modern era, including the need to adapt to changing social and political norms.
- Many monarchies have had to evolve to accommodate changes such as the end of absolute monarchy and the introduction of democratic reforms.
- The British monarchy is one of the most well-known and respected monarchies, with a history dating back over 1,000 years.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of a king next in line to the throne is a complex and fascinating topic that has been shaped by history, culture, and politics. While monarchies continue to play an important role in many countries around the world, they must also adapt to changing social and political norms. By understanding the rules of succession and the challenges facing monarchies, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the rich history and cultural significance of these institutions.
What is the purpose of the rules of succession in a monarchy?
+The purpose of the rules of succession is to ensure a smooth transition of power and prevent disputes over who should inherit the throne.
How do monarchies adapt to changing social and political norms?
+Monarchies adapt to changing social and political norms by evolving their institutions and practices to accommodate new values and expectations. This can involve reforms such as the introduction of democratic reforms, the recognition of the rights of women and minorities, and the establishment of a constitutional monarchy.
What is the significance of the British monarchy in modern times?
+The British monarchy is significant in modern times because it continues to play an important role in British society and culture. The monarchy also serves as a symbol of national identity and unity, and is an important part of the country’s history and heritage.
