When examining the evolution of higher education admissions in the United States, James Madison University emerges as a compelling case study. Renowned for its commitment to accessible education and competitive programs, Madison's admission statistics over the past decade reflect broader national trends and localized institutional strategies. Tracing its historical roots back to its founding in 1908 as a normal school, Madison has traversed significant transformations—transitioning from a small teacher training college to a comprehensive institution with over 20,000 students. These shifts have profoundly impacted its admission landscape, influenced by demographic changes, policy reforms, and evolving university priorities. Understanding Madison’s admission metrics provides insight into not only institutional growth but also the broader dynamics governing college accessibility and selectivity in the modern era.
Historical Foundations and Evolution of James Madison University Admissions

The origins of James Madison University (JMU) are rooted in the early 20th century, designed initially to serve regional educational needs. Its founding mission emphasized teacher training, which reflected the societal priorities of that era. As Virginia’s educational landscape grew increasingly competitive, Madison gradually expanded its academic offerings, necessitating shifts in its admission policies. During the post-World War II period, the GI Bill and demographic booms in the 1960s prompted a substantial increase in applicant pools. Notably, the university’s transition to a public comprehensive university in the late 20th century ushered in a more holistic admissions approach, balancing academic metrics with extracurricular and socioeconomic factors.
This historical perspective underscores how major societal and policy shifts have shaped Madison’s admission standards. From restrictive early entry criteria focused solely on academic excellence to today’s multifaceted evaluation processes, the university’s evolving admission statistics mirror these broader trends. As with many institutions, Madison navigated challenges like increasing applicant volumes against finite campus resources, leading to the adoption of strategic enrollment management practices.
Current Admission Overview: Trends, Data, and Student Profile

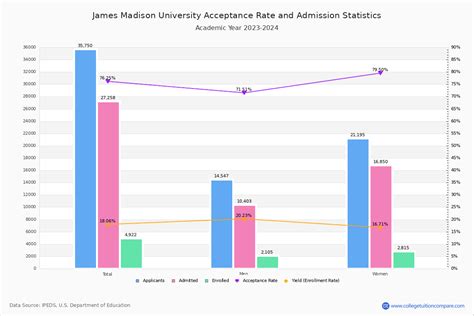
Analyzing recent admission data reveals a nuanced picture of Madison’s contemporary selectivity and diversity. As of Fall 2023, the university received over 22,000 applications, accepting approximately 70%, which positions it as a moderately selective institution. The demographics of admitted students exhibit notable diversity; for instance, the undergraduate enrollment breakdown includes students from over 40 states and multiple countries, reflecting its expanding national and international appeal.
One key metric—admissions rate—has fluctuated within a range of 68-72% over recent years, indicating a stable yet increasingly competitive environment. Average SAT scores for admitted students hover around 1160-1180, and the middle 50% ACT scores range from 23 to 27, suggesting Madison’s commitment to academic quality while maintaining accessible admission standards. The high school GPA median tends to sit at approximately 3.5 on a 4.0 scale, emphasizing the importance of consistent academic performance.
Moreover, the university’s admissions process accounts for holistic factors, such as leadership, community service, and personal statements. Data-driven insights underscore that the admissions committee increasingly emphasizes diverse experiences and socioeconomic mobility, aligning with broader institutional goals of inclusivity. This strategic shift reflects an understanding that holistic review enhances institutional reputation and student success outcomes.
Admissions Strategy and Predictive Metrics
Madison’s admissions strategy leverages a combination of quantitative data and holistic review to select a class that aligns with its mission of fostering a diverse, vibrant community. Predictive analytics models indicate that high school GPA and standardized test scores remain significant predictors of college performance, but factors such as extracurricular involvement and personal essays increasingly influence admission decisions.
One notable innovation has been the adoption of test-optional policies, first introduced in 2020, which contributed to a 15% increase in applications and broader demographic representation. The decision to prioritize holistic review, supported by institutional research, aims to balance academic preparedness with the value of diverse lived experiences—an approach that resonates with modern enrollments strategies aimed at enhancing campus richness and academic excellence.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Acceptance Rate | Approximately 70% in 2023, stable over recent years |
| Average SAT Score (Middle 50%) | 1160–1180 |
| Average ACT Score (Middle 50%) | 23–27 |
| High School GPA Median | around 3.5 |
| Application Volume | Over 22,000 applications in Fall 2023 |

Comparative Perspectives: Madison versus Peer Institutions
Comparing Madison’s admission statistics with peer institutions in the Atlantic Coast Conference and the broader Virginia higher education system underlines its distinctive positioning. Universities like Virginia Commonwealth University and James Madison face similar demographic pressures but differ in selectivity and diversity metrics. Madison’s acceptance rate sits at a median point among peers, indicating a balanced approach that maximizes access without compromising academic standards. Where Madison excels is in its ability to attract high-achieving, diverse students, evidenced by its graduation rates and post-graduate employment statistics.
This comparative analysis draws attention to strategic differentiators: Madison’s initiative for inclusive excellence, encompassing outreach in underserved communities and generous merit scholarships, has boosted its diversity indexing. The institution’s ratio of in-state to out-of-state students, approximately 60:40, demonstrates a healthy geographical and cultural mix—a strategic outcome of targeted recruitment and scholarship programs.
Implications of Admission Trends for Future Strategic Planning
The trajectory of Madison’s admission statistics suggests a deliberate pursuit of growth in selectivity and student quality. Innovations like predictive analytics, expanded recruitment beyond traditional feeder regions, and continued emphasis on holistic review serve to sustain its competitive edge. Additionally, demographic data indicates a steadily rising representation of historically underrepresented groups, hinting at a future where Madison continues to balance access with academic rigor.
Emerging challenges include managing capacity constraints and ensuring quality assurance amid increasing application volumes. Strategic initiatives, such as expanding virtual outreach, leveraging AI-driven enrollment models, and fostering community partnerships, are set to be pivotal in maintaining Madison’s reputation and meeting its growth targets.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of Madison’s Admission Commitments
James Madison University’s admission statistics encapsulate a story of adaptation and resilience. From its humble beginnings rooted in teacher training to its current role as a dynamic, inclusive institution, Madison reflects broader national trends and innovative practices that dictate higher education access. Its ongoing evolution—marked by a sophisticated balance of holistic review, strategic outreach, and data-informed decision making—positions it favorably amidst competitive Virginia and national markets. As the institution continues to refine its admissions processes, embracing technological advancements and diversity imperatives, Madison exemplifies how university strategies can effectively navigate changing societal expectations while fostering academic excellence.
Key Points
- Madison's admission rate (~70%) balances accessibility with selectivity, reflecting strategic policy evolution.
- Test-optional policies have increased diversity and application volume, aligning with modern holistic review paradigms.
- Demographic trends indicate rising diversity and geographical reach, bolstered by targeted outreach and scholarships.
- Comparative positioning reveals Madison’s balanced approach relative to peer institutions in Virginia and the broader region.
- The future of Madison admissions hinges on technological integration and maintaining quality amid expansion pressures.
How have Madison’s admission standards changed over the last decade?
+Madison has shifted from primarily academic metrics to a more holistic review process, with test-optional policies increasing application diversity and volume while maintaining overall selectivity around 70% acceptance.
What role does demographic diversity play in Madison’s admissions?
+Increasing emphasis on diversity and inclusion has led Madison to target underrepresented groups through outreach and scholarships, enhancing campus cultural richness and aligning with institutional equity goals.
What future trends are likely to influence Madison’s admissions strategy?
+Advancements in AI, predictive analytics, and remote engagement will play vital roles in optimizing admissions, alongside ongoing efforts to improve diversity, equity, and access.