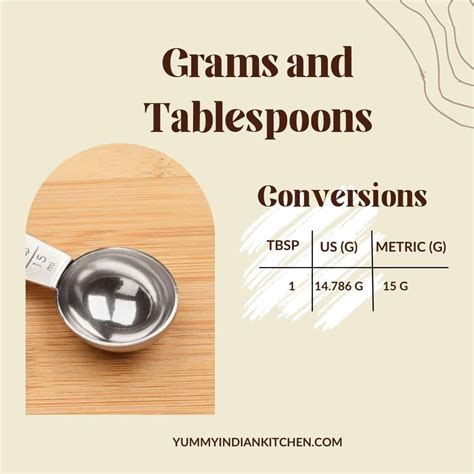
The relationship between grams and tablespoons is not straightforward because it depends on the density of the substance being measured. However, for many common ingredients, approximate conversions can be used. Understanding these conversions is crucial in cooking and baking, where precision can significantly affect the final product.
General Conversion Guidelines

For dry ingredients like flour, sugar, and cocoa powder, the weight in grams per tablespoon can vary. For example, 1 tablespoon of all-purpose flour is approximately 7.6 grams, while 1 tablespoon of granulated sugar is about 15 grams. These values can vary slightly based on how the ingredients are packed or sifted.
Conversion Factors for Common Ingredients
Here are some approximate conversion factors for common ingredients from tablespoons to grams:
| Ingredient | Grams per Tablespoon |
|---|---|
| All-purpose Flour | 7.6 grams |
| Granulated Sugar | 15 grams |
| Brown Sugar | 13 grams (packed) |
| Cocoa Powder | 8 grams |
| Butter | 14 grams |

Understanding Density and Its Impact on Measurements
Density plays a crucial role in the conversion between volume and weight measurements. Ingredients with higher densities will have more grams per tablespoon, while less dense ingredients will have fewer grams per tablespoon. This principle explains why different ingredients have different gram-to-tablespoon conversion rates.
Practical Applications of Grams to Tablespoons Conversions
In practical terms, understanding these conversions is vital for achieving consistent results in cooking and baking. A small discrepancy in measurement can significantly affect the texture, flavor, and overall success of a dish. For instance, in baking, too much or too little flour can alter the structure of cakes and pastries.
Key Points
- The conversion from tablespoons to grams depends on the ingredient's density.
- Common ingredients like flour, sugar, and butter have approximate gram weights per tablespoon that can be used for conversions.
- Using a digital kitchen scale is the most accurate method for measuring ingredients, especially in professional cooking and baking.
- Different ingredients have unique conversion factors due to variations in density.
- Precise measurements are critical in baking for achieving the desired texture and flavor.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, while there isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer to how many grams are in a tablespoon due to the varying densities of different substances, understanding the specific conversion rates for common ingredients is essential for both amateur and professional cooks and bakers. As culinary practices evolve, the importance of precision and the use of digital tools like kitchen scales will continue to grow, allowing for more intricate and consistent creations in the kitchen.
Why are precise measurements important in cooking and baking?
+Precise measurements are crucial because they directly affect the final product’s texture, flavor, and appearance. Small discrepancies can lead to significant differences in the outcome, especially in baking.
How can I ensure accurate conversions between tablespoons and grams?
+Using a digital kitchen scale is the most accurate method. However, for those relying on conversions, consulting a reliable conversion chart or using online tools that provide ingredient-specific conversions can help.
Are there any ingredients for which the conversion from tablespoons to grams is more critical than others?
+Yes, ingredients like leavening agents (baking powder, baking soda), yeast, and salt require very precise measurements because they have a profound impact on the chemical reactions and, consequently, the final product in baking and cooking.