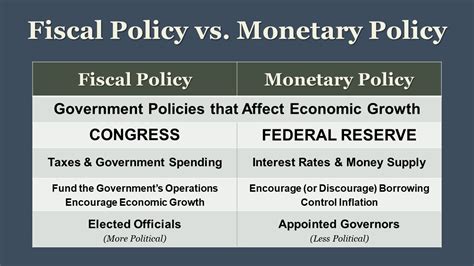
In the complex realm of economic stewardship, fiscal policy stands as a pivotal instrument wielded by governments to influence macroeconomic stability, growth, and public trust. Among its various approaches, conservative fiscal policy often emerges as a contentious yet essential debate within economic discourse. Contrary to prevalent misconceptions, mastering conservative fiscal policy is not merely about austerity; it involves a nuanced, data-driven strategy aimed at fostering sustainable economic strength. This article seeks to debunk myths surrounding conservative fiscal ideology, dissecting its core principles, practical implementations, and long-term benefits with evidence-based analysis rooted in economic theory and historical precedent.
Understanding Conservative Fiscal Policy: Foundations and Misconceptions

At its essence, conservative fiscal policy emphasizes prudent government spending, disciplined taxation, and sustainable debt management, prioritizing economic stability over short-term populist measures. Many equate it solely with austerity or austerity-like measures, overlooking its broader scope involving strategic investment, systematic tax reform, and risk mitigation. The misconception persists that fiscal conservatism stifles economic growth, yet empirical data often contradicts this view. For example, nations with disciplined fiscal practices frequently experience lower inflation, reduced public debt, and higher investor confidence, which collectively catalyze sustainable growth.
Core Principles of Conservative Fiscal Policy
Fundamentally, conservative fiscal policy is grounded in several key tenets:
- Balanced Budgets: Avoiding deficits that could lead to unsustainable debt burdens.
- Strategic Taxation: Maintaining a tax structure that incentivizes productivity and investment while ensuring fiscal responsibility.
- Reduced Public Debt: Prioritizing debt reduction to minimize interest costs and fiscal vulnerability.
- Long-term Investment: Focusing on infrastructure, education, and innovation, but within sustainable financial bounds.
- Minimalistic Intervention: Limiting government involvement in sectors where private enterprise can operate efficiently.
Historical Case Studies Undermining Myths of Economic Harm
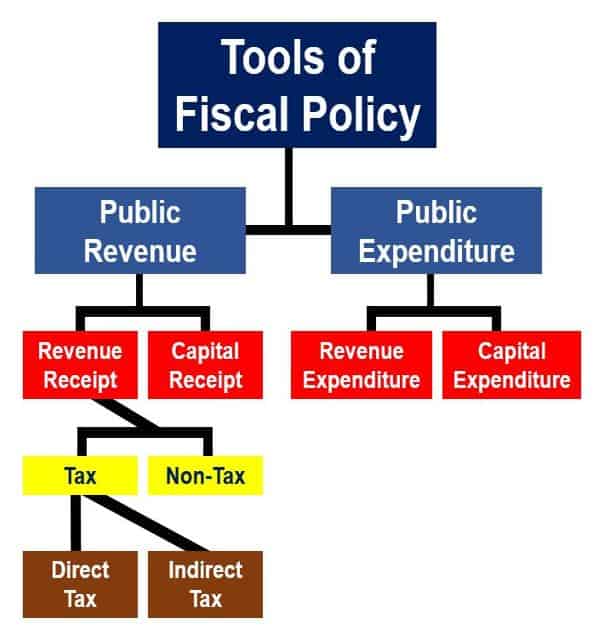
Historical analysis reveals that several countries exemplify how disciplined fiscal policies underpin economic resilience. For instance, during the 1990s, Canada implemented a series of fiscal reforms emphasizing balanced budgets and debt reduction, leading to more robust economic growth and stability. Similarly, New Zealand in the late 20th century adopted conservative fiscal reforms that curbed inflation and improved credit ratings, enabling sustainable expansion.
Debunking the Myth that Fiscal Conservatism Stifles Growth
Contrary to the misconception that fiscal austerity hampers economic dynamism, data indicates that countries maintaining disciplined fiscal policies often outperform their highly indebted counterparts during economic downturns. For example, during the European debt crisis, nations such as Germany and the Netherlands—which adhered to conservative fiscal principles—demonstrated fiscal resilience, with stronger GDP growth and employment recovery compared to less disciplined economies.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Debt-to-GDP Ratio | Germany’s ratio: approximately 60% in 2023, compared to Greece at over 170%. |
| Economic Growth Rate | Germany’s average GDP growth post-2010: ~1.5–2%, versus several European peers with higher debt levels and slower growth. |
| Inflation Rates | Germany consistently maintained low inflation, around 1-2%, while others experienced volatile inflationary episodes linked to fiscal mismanagement. |

Strategic Implementation: From Theory to Practice
Effective mastery of conservative fiscal policy involves translating principles into practical strategies. Governments must prioritize fiscal transparency and data-driven decision-making. For instance, adopting balanced budget rules with clear thresholds can anchor fiscal responsibility. Moreover, employing automatic stabilizers—such as progressive taxation and unemployment benefits—can cushion economic cycles without jeopardizing fiscal stability.
Fiscal Policy Tools and Innovations
Contemporary policymakers leverage tools like fiscal rules, debt ceilings, and performance-based budgeting to uphold conservative principles. Advanced analytics and real-time fiscal monitoring further enable timely adjustments. Additionally, strategic privatizations and public-private partnerships can deliver public goods efficiently, aligning with conservative tenets of minimizing unnecessary government expenditure.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Fiscal Rule Adoption | Approximately 65 countries adopted binding fiscal rules in 2022, indicating widespread institutional commitment. |
| Debt Ceiling Usage | In the U.S., the debt ceiling has been periodically revised, but disciplined processes aim to prevent excessive accumulation. |
| Investment in Public Goods | Private sector participation as a share of infrastructure investment: over 40% in advanced economies, complementing fiscal prudence. |
Addressing Criticisms and Limitations
Opponents of conservative fiscal policy often cite concerns about reduced social spending and perceived inflexibility during downturns. Yet, evidence indicates that smart fiscal conservatism emphasizes targeted investments and fiscal buffers to mitigate such risks. Moreover, overreliance on short-term stimulus measures without regard for fiscal sustainability can worsen crises, as seen in early 2000s speculative bubbles and recent inflationary surges.
Balancing Fiscal Discipline and Economic Needs
Achieving an optimal balance requires consistent policy review, stakeholder engagement, and flexible frameworks that prioritize long-term health over immediate gains. Establishing fiscal resilience through diversified revenue streams and debt restructuring options empowers policymakers to adapt to unforeseen shocks without abandoning core conservative principles.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Social Spending Impact | Countries with prudent fiscal policies, like Australia, maintain social safety nets while avoiding excessive debt, ensuring social stability. |
| Economic Shock Response | During COVID-19, some nations with conservative frameworks responded with targeted support, avoiding catastrophic debt levels. |
| Long-term Fiscal Health | Investment in education and infrastructure correlated with higher productivity, even under fiscal constraints, demonstrated by Singapore’s performance. |
Conclusion: Mastery as a Catalyst for Sustainable Economic Strength

Mastering conservative fiscal policy does not equate to rigid austerity but involves cultivating a strategic mindset focused on long-term stability, risk management, and efficiency. Evidence affirms that disciplined fiscal stewardship provides a solid foundation for resilient, vibrant economies capable of weathering global uncertainties. Demystifying myths and embracing data-informed practices enable policymakers to deploy conservative principles effectively, steering nations toward enduring prosperity and fiscal sanity.
Key Points
- Evidence-based fiscal discipline fosters sustainable growth and investor confidence.
- Historical precedents demonstrate that responsible debt management reduces crisis vulnerability.
- Practical implementation involves innovative tools and transparent frameworks.
- Strategic flexibility facilitates balancing fiscal health with social and economic needs.
- Mastery elevates fiscal policy from reactive measures to strategic enablers of prosperity.
What are the main benefits of conservative fiscal policy?
+Conservative fiscal policy promotes long-term economic stability, reduces debt burdens, lowers inflation rates, and boosts investor confidence—all essential for sustainable growth.
Can conservative fiscal policies be effective during economic downturns?
+Yes, when combined with targeted strategies and resilient frameworks, disciplined fiscal policies can support economic recovery without exacerbating debt issues or creating future vulnerabilities.
How do historical examples support the case for fiscal discipline?
+Historical cases like Canada in the 1990s and New Zealand in the 1980s show that disciplined fiscal reforms lead to lower debt levels, stable inflation, and greater economic resilience over time.
What challenges are associated with implementing conservative fiscal policies?
+Challenges include balancing social spending needs, avoiding overly restrictive measures, ensuring transparency, and maintaining political consensus amidst diverse economic conditions.
Related Terms:
- Limited Government Spending
- Fiscal conservatism meaning
- Fiscal conservative examples
- Fiscally conservative socially liberal meaning
- Fiscal conservatism vs economic liberalism
- Fiscal conservative beliefs