The Chicago metropolitan area, often branded as the "Second City," has long been a magnet for migration, economic activity, and demographic shifts within the United States. Despite facing challenges such as economic downturns, suburban sprawl, and shifting industrial bases, recent years have unveiled a pattern of population growth surprises that demand critical analysis. These unexpected trends mirror complex interplay among urban policies, socio-economic factors, infrastructure investments, and broader national migration patterns, all of which can be comprehended better through a systems thinking lens.
Unraveling Population Growth Dynamics in the Chicago Metro Area
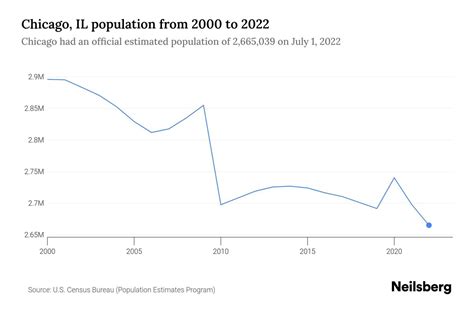
The population trends in Chicago’s metro region, covering Cook, DuPage, Lake, Will, and Kane counties among others, reveal a nuanced story. Although some historical data suggested stagnation or decline due to deindustrialization and suburban flight, recent datasets indicate a surprising resilience and even growth in specific demographic segments. Understanding these shifts necessitates a comprehensive exploration of interconnected drivers such as immigration, return migration, housing developments, economic diversification, and infrastructural resilience.
Population Shifts: Beyond the Overall Numbers
Much of the recent growth in Chicago’s metro area is driven by diversification within its demographic fabric. While the city of Chicago itself has experienced periods of stagnation and decline intertwined with neighborhood-level gentrification, suburban counties have witnessed a countertrend of influx, especially among Hispanic, Asian, and younger professional populations. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, from 2010 to 2022, the metropolitan area’s population increased by approximately 2%, defying earlier projections that forecasted continued decline.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Overall Population Change | +2% from 2010 to 2022 in the metro region, contrasting with nationwide trends of urban depopulation |
| Population of Chicago City | Relatively flat, with minor fluctuations, amid neighborhood-level gentrification and displacement |
| Suburban Growth | Significant increases observed in DuPage (+4%), Kane (+3.5%), Will (+3%), and Lake (+2.5%) counties |
| Immigration Impact | Estimated at 15% of overall suburban growth, primarily from Latin America and Asia |

Key Factors Driving Population Surprises in Chicago Metro Area

Several interconnected components collaboratively shape recent population growth patterns that may seem counterintuitive. These include economic diversification, housing innovations, transportation infrastructure, educational opportunities, and immigrant networks—all influencing each other within the urban-regional system.
Economic Resilience and Diversification
Traditionally reliant on manufacturing and heavy industry, Chicago’s economy has pivoted toward healthcare, technology, finance, and logistics sectors. The city’s emergence as a hub for health sciences and tech startups, supported by initiatives such as the Illinois Science & Technology Park, has attracted young professionals and entrepreneurs. This economic pivot acts as a catalyst for population retention and attraction, especially for highly educated cohorts.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Employment Growth | Healthcare and tech sectors grew by approximately 6% and 8% respectively between 2018-2022 |
| Labor Market Participation | Increased in suburban counties, with a notable rise among minority workers |
Housing Innovation and Urban Redevelopment
Contrary to expectations of urban decline, the Chicago metro has witnessed innovative housing solutions, including transit-oriented developments, micro-apartments, and rehabilitated historic buildings. The expansion of the ‘Magnet’ program, offering incentives for affordable housing and mixed-use developments, has contributed to attracting diverse populations, especially young adults and immigrant families seeking affordability and access to urban amenities.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Housing Price Trends | Median home prices in suburbs increased by 3.5% annually post-2019, while affordability improved relative to coastal cities |
| New Construction Permits | Increase of approximately 9% in suburban counties, indicating active investment in residential infrastructure |
Transportation and Infrastructure Investments
Enhanced transit options, including expanded Metra services and the ongoing development of the Red and Purple Lines, facilitate urban-suburban mobility. Such infrastructure investments lower barriers to suburban living while maintaining city access, creating a feedback loop that sustains population growth across the metro area.
Key Points
- Resilient economic diversification has mitigated urban decline and attracted new residents.
- Innovative housing strategies and redevelopment projects enhance urban and suburban attractiveness.
- Transportation infrastructure improvements create positive feedback, fostering sustained growth.
- Immigrant and minority communities continue to play pivotal roles in demographic resilience.
- Interdependencies among these elements prompt a systemic analysis for future urban planning.
Interconnected Systems and Emerging Trends
The recent population trajectory in Chicago’s metro region exemplifies how multiple systems interact dynamically. For example, economic diversification fuels housing demand, which in turn affects transportation planning. Meanwhile, immigrant networks contribute to labor market vitality, reinforcing economic resilience. This interconnectedness leads to emergent phenomena—such as regional growth surprises—that defy linear prediction models.
Migration Patterns and Policy Implications
Return migration of native-born Chicagoans, propelled by remote work, combined with international immigration, creates a feedback loop encouraging urban re-investment. Policies incentivizing affordable housing and transit expansion further stimulate demographic stability and growth, producing a resilient urban fabric. Recognizing these patterns informs strategic investments and governance aimed at maintaining balanced growth.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Remote Work Trends | Survey data indicates a 12% increase in remote-capable jobs in the metro region between 2020-2023 |
| Immigration Data | 15,000 new immigrant arrivals annually since 2015, primarily from Latin America and Asia |
Limitations, Challenges, and Future Outlook
Despite the positive surprises, Chicago’s population growth faces potential headwinds: economic downturns, climate-related disasters, and demographic aging could disrupt current trends. Additionally, gentrification and displacement pose social equity concerns that require nuanced policy responses. Anticipating these interconnected challenges via a systems approach enables more holistic, adaptable strategies for sustainable growth.
Conclusion: Embracing Complexity in Urban Planning
The population growth surprises within Chicago’s metro area exemplify how understanding the web of socio-economic, infrastructural, and policy factors through a systems thinking lens is vital. These dynamic interdependencies necessitate integrated planning approaches that recognize feedback mechanisms, nonlinearity, and emergent behaviors—paving the way for resilient urban futures that capitalize on their inherent interconnectedness.
What are the main drivers behind recent population growth in Chicago’s suburbs?
+Key drivers include economic diversification, innovative housing development, improved transportation infrastructure, and the influx of immigrant communities, all creating a reinforcing system that sustains population growth.
How does migration influence Chicago’s demographic changes?
+Migration from international sources and internal return migration of native-born residents contribute significantly to demographic replenishment, often mediated by policy incentives, economic opportunity, and lifestyle factors facilitated by infrastructure developments.
What challenges could disrupt future growth in the Chicago metropolitan area?
+Potential headwinds include economic recessions, climate disasters, demographic aging, social displacement, and policy misalignments—all of which can alter the interconnected system and its growth trajectory.
