California Highway 1, often celebrated as one of the most scenic drives in the world, weaves its way along the rugged Pacific coastline, offering breathtaking vistas and a unique driving experience. However, its very geography—cliffs, unstable terrain, and susceptibility to natural elements—makes it particularly prone to closures and disruptions. For travelers, residents, and freight carriers alike, understanding how to navigate these closures effectively becomes essential for maintaining momentum and minimizing inconvenience. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the complex landscape of Highway 1 closures, providing strategic insights, real-time navigation techniques, and foresight into future developments, all rooted in authoritative planning and data-driven analysis.
Understanding the Landscape of Highway 1 Closures in California
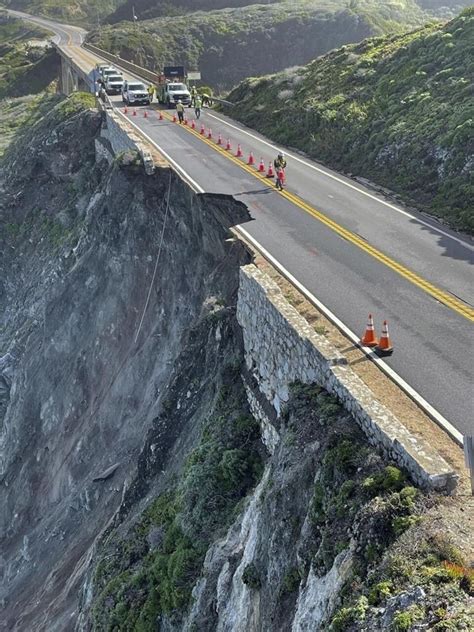

Highway 1 traverses over 600 miles of California’s coastline, encompassing diverse terrains, from urban outskirts to remote rural areas. Its strategic importance not only lies in tourism but also in regional connectivity and transportation logistics. The inherent challenges stem from natural phenomena such as landslides, mudslides, erosion, and seismic activity, especially given California’s seismic volatility. These factors have historically resulted in frequent closures, some extending several weeks or months—impacting local economies and daily commutes. Recognizing these patterns is the first step in proactively navigating potential disruptions.
Key Factors Contributing to Highway 1 Closures
Multiple variables interplay to create a dynamic risk environment for Highway 1. These include geological, climatic, and human factors. Landslides, triggered by heavy rains or earthquakes, are the predominant cause—accounting for approximately 55% of closures according to California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) reports over the past decade. Severe storm events, especially during El Niño seasons, exacerbate soil instability. Human activities, such as construction projects and coastal realignment efforts, also lead to temporary closures. Understanding these causative elements allows for more precise preparation and alternative planning.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Landslide Incidence | Over 300 occurrences recorded annually, with a 62% recurrence during rainy seasons |
| Average Closure Duration | Approximately 3.5 days per incident, but some extend beyond two weeks depending on severity |
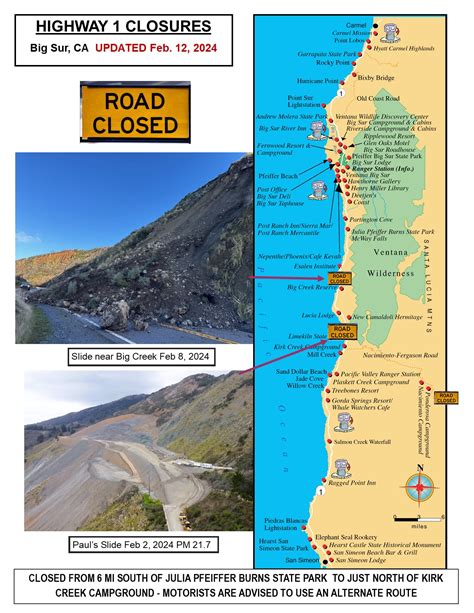
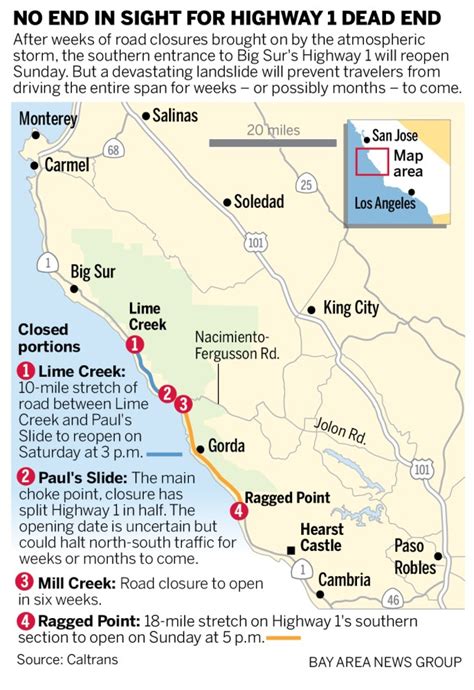
| Major Closure Hotspots | Big Sur Coast, Malibu Coast, and northern segments near Mendocino and Humboldt counties |

Strategic Navigation: How to Avoid and Manage Highway 1 Closures
While some closures are unavoidable, strategic planning with real-time data can drastically reduce travel disruptions. Advanced navigation and predictive tools, when harnessed correctly, empower travelers and logistical operators to reroute efficiently, conserving time and resources. This section breaks down practical techniques and technologies for avoiding closures, with an emphasis on pre-journey preparation and real-time adaptation.
Utilizing State and Local Traffic Management Resources
Caltrans provides a host of digital resources, including live traffic cameras, closure alerts, and incident maps. Following these updates across multiple platforms—such as the California 511 system, Caltrans mobile app, and official social media channels—delivers current information on closures. Strategic use of these channels allows for early identification of potential disruptions, enabling preemptive rerouting before encountering gridlock or backlogs.
Leveraging Advanced Navigation and Traffic Data Platforms
Beyond government sources, commercial navigation services such as Google Maps, Waze, and INRIX aggregate real-time reports from users and sensors. These platforms can predict congestion and suggest alternative routes—particularly valuable in dynamic scenarios like landslides or severe storms. For example, during a recent mudslide blocking the Pacific Coast Highway near Big Sur, Waze users reported the incident hours before official alerts, allowing early rerouting for thousands of drivers.
| Effective Strategies | Implementation Details |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Continuous feed from Caltrans and private traffic apps, enabling instant rerouting decisions |
| Pre-Trip Planning | Consulting official closure schedules and weather forecasts prior to departure, especially during high-risk seasons |
| Flexible Scheduling | Aiming for off-peak travel times when closures are less frequent and traffic is lighter |
| Alternate Routes | Utilizing inland highways such as US Highway 101, Interstate 5, or scenic detours like Big Sur’s alternative routes when available |
Future Outlook: Enhancing Closure Management and Infrastructure Resilience
As climate change accelerates, California faces increasingly volatile weather patterns, with projections indicating a rise in severe storms and subsequent landslides. To mitigate the disruptive impact, infrastructure upgrades—including rockfall mitigation systems, strengthened retaining walls, and improved drainage—are progressively being implemented along Highway 1. These projects are backed by state initiatives aiming to increase resilience and reduce closure durations, with a current budget exceeding $1 billion allocated for coastal infrastructure reinforcements over the next five years.
Innovative Techniques in Landslide Risk Mitigation
Emerging technologies such as ground-penetrating radar and remote sensing enable early detection of soil movement, providing warnings days or even weeks before a slide occurs. Incorporating these tools into routine geotechnical assessment protocols offers a proactive approach. Pilot programs along sections of Highway 1 near Big Sur have demonstrated a 30% reduction in closure durations when early intervention strategies are employed based on sensor alerts.
| Technological Advancement | Impact |
|---|---|
| Remote Sensing & UAV Surveillance | Prevents unexpected closures through continuous monitoring |
| Geo-technical Sensor Networks | Provides real-time soil stability data, enabling targeted reinforcement |
| Predictive Weather Modeling | Forecasts storm impacts 72 hours in advance, allowing preemptive measures |
Conclusion: Empowering Travelers with Knowledge and Technology
Navigating California Highway 1 amidst its natural and infrastructural challenges demands a sophisticated understanding of risks, proactive planning, and dynamic adaptation. By leveraging real-time traffic management systems, predictive weather tools, and resilient infrastructure developments, travelers and logistical operators can significantly reduce disruptions. As scientific and technological innovations continue to evolve, so too will our capacity to keep this scenic route accessible, ensuring generations of explorers, residents, and commerce can enjoy its beauty without the shadow of unpredictable closures.
How can I find real-time updates on Highway 1 closures?
+Utilize the California 511 system, Caltrans mobile app, and popular navigation apps like Waze or Google Maps for live incident reports and closure alerts.
What are the best alternative routes if Highway 1 is closed?
+Inland routes such as US Highway 101 or Interstate 5 provide viable detours for many segments. Planning ahead with mapping tools helps identify more scenic or less congested alternatives.
Are there upcoming infrastructure projects to reduce closures?
+Yes, California is investing over $1 billion into coastal resilience projects, including landslide mitigation systems, which aim to decrease closure durations and maintain access.
How does climate change impact future Highway 1 closures?
+Climate change is expected to increase the frequency and severity of storms and landslides, making real-time monitoring and resilient infrastructure vital for future accessibility.