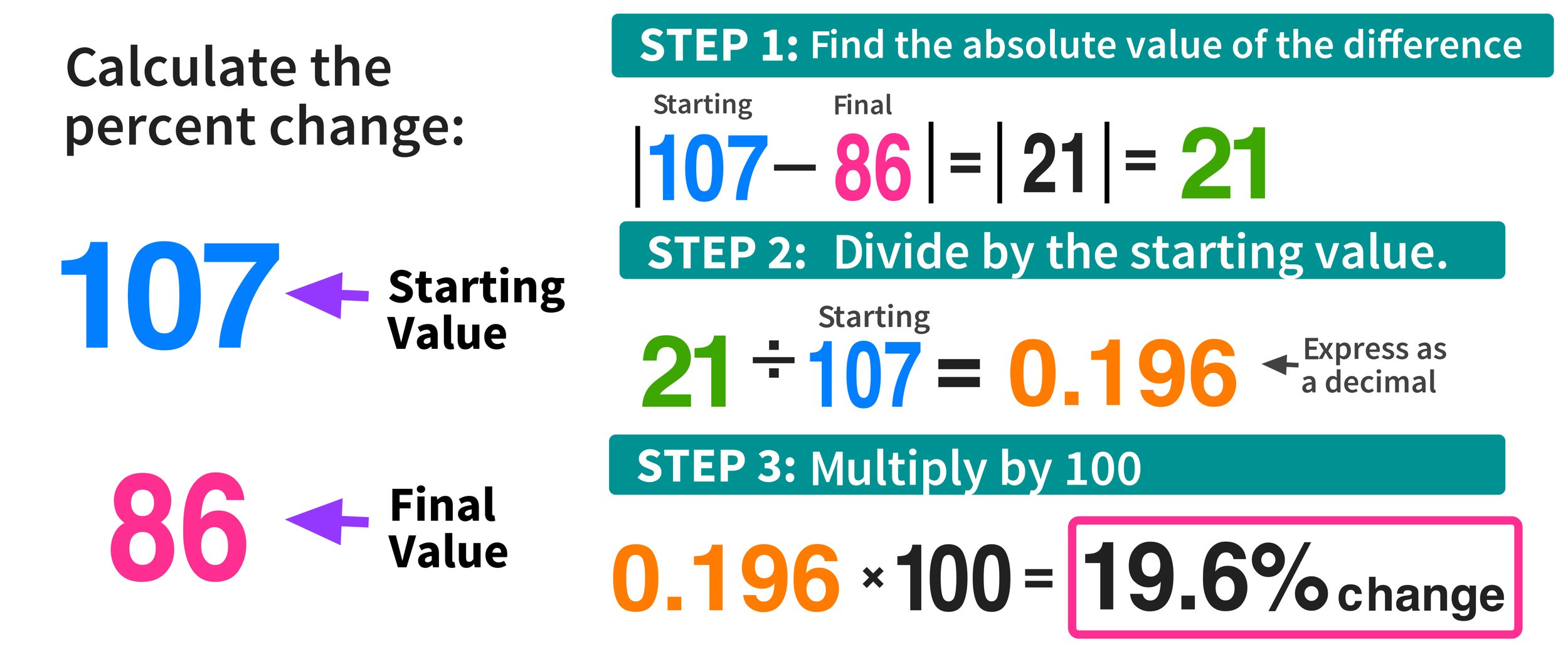
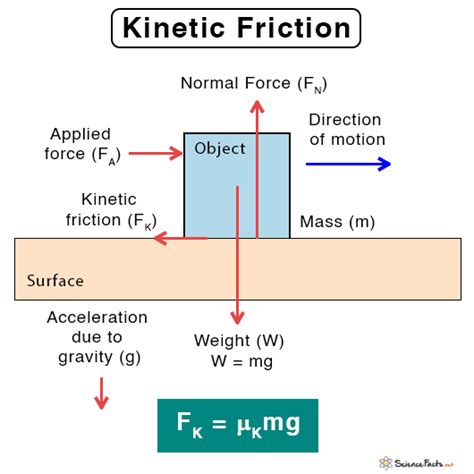
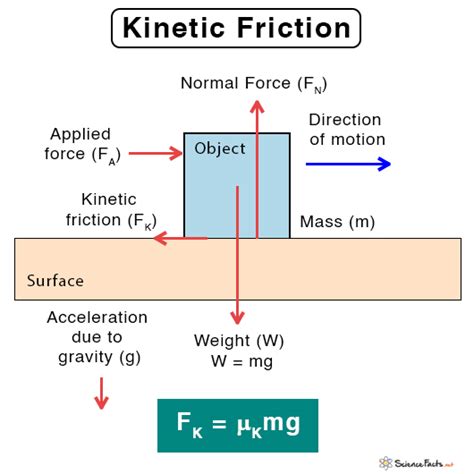
The concept of kinetic friction is a fundamental aspect of physics, playing a crucial role in understanding the behavior of objects in motion. Kinetic friction, also known as dynamic friction, is the force that opposes the motion of an object when it is already moving. Unlike static friction, which prevents an object from moving, kinetic friction acts to slow down the object. To calculate kinetic friction, we need to understand its underlying principles and the formula that governs its calculation.
Understanding Kinetic Friction

Kinetic friction is a force that arises from the interaction between two surfaces that are in motion relative to each other. The magnitude of the kinetic frictional force depends on two main factors: the normal force (the force exerted by one surface on the other, perpendicular to the surfaces) and the coefficient of kinetic friction (a value that depends on the materials of the two surfaces). The coefficient of kinetic friction is typically denoted by the symbol μk and is usually less than the coefficient of static friction.
Formula for Calculating Kinetic Friction
The formula to calculate the kinetic frictional force (Fk) is given by:
Fk = μk * N
Where:
- Fk is the kinetic frictional force,
- μk is the coefficient of kinetic friction, and
- N is the normal force.
The normal force (N) can be calculated as the weight of the object (mg), where m is the mass of the object and g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s^2 on Earth), assuming the object is moving on a horizontal surface.
| Parameter | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fk | Kinetic frictional force | Newton (N) |
| μk | Coefficient of kinetic friction | Dimensionless |
| N | Normal force | Newton (N) |
| m | Mass of the object | Kilogram (kg) |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity | Meter per second squared (m/s^2) |
Example Calculation
Consider a block of wood with a mass of 5 kg being pulled across a horizontal floor. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the wood and the floor is 0.2, and assuming the block is moving at a constant velocity (so the net force acting on it is zero), we can calculate the kinetic frictional force acting on the block.
First, calculate the normal force (N), which in this case is the weight of the block:
N = m * g = 5 kg * 9.81 m/s^2 = 49.05 N
Then, calculate the kinetic frictional force (Fk):
Fk = μk * N = 0.2 * 49.05 N = 9.81 N
This means the kinetic frictional force opposing the motion of the block is 9.81 Newtons.
Key Points
- Kinetic friction is the force opposing the motion of an object that is already moving.
- The formula for kinetic friction is Fk = μk * N, where Fk is the kinetic frictional force, μk is the coefficient of kinetic friction, and N is the normal force.
- The normal force (N) is typically the weight of the object (mg) for objects moving on horizontal surfaces.
- The coefficient of kinetic friction (μk) depends on the materials of the surfaces in contact and is usually determined experimentally or from reference tables.
- Accurate calculation of kinetic friction requires knowing the specific coefficient of kinetic friction for the surfaces involved.
Implications and Applications
Understanding and calculating kinetic friction has numerous practical implications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and everyday life. For instance, in the design of vehicles and machinery, kinetic friction plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and performance of moving parts. Similarly, in sports, the interaction between athletic footwear and different surfaces can significantly affect performance, making the study of kinetic friction valuable for optimizing athletic equipment.
Furthermore, kinetic friction is essential in the context of safety, particularly in the design of braking systems in vehicles and the calculation of stopping distances. The ability to predict and manage kinetic friction can lead to the development of safer and more efficient technologies.
What is the difference between kinetic and static friction?
+Kinetic friction occurs when an object is already in motion, opposing its movement, whereas static friction prevents an object from moving in the first place. Static friction is typically stronger than kinetic friction.
How do you determine the coefficient of kinetic friction?
+The coefficient of kinetic friction is usually determined through experimental measurements or by consulting reference tables that list coefficients for various material combinations.
Why is kinetic friction important in engineering and design?
+Kinetic friction is crucial in the design of moving parts, as it affects the efficiency, performance, and longevity of machines and vehicles. Understanding and managing kinetic friction can lead to more efficient and safer designs.
In conclusion, the calculation of kinetic friction is a fundamental aspect of understanding the dynamics of moving objects. By applying the formula Fk = μk * N and considering the specific coefficients of kinetic friction for the materials involved, one can accurately determine the kinetic frictional force acting on an object. This knowledge is not only essential for theoretical physics but also has significant practical implications in engineering, design, and everyday applications.