
SpaceX
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy could launch astronauts to the Moon, says NASA admin
Despite contrary comments made one week prior, NASA administrator Jim Bridenstine has affirmed – this time in no uncertain terms – that a two-week study investigating commercial options for launching the Orion spacecraft to the Moon has concluded that Falcon Heavy could be the only practical option if NASA chooses to proceed.
Due to fundamental performance and logistical constraints of both Delta IV Heavy and Falcon Heavy, as well as a lack in confidence in certain alternative paths, NASA now believes that a commercial option – Falcon Heavy – exists, but would face multiple major challenges, to the extent that Bridenstine indicated it would not be able to make the 2020 launch deadline with an unspecified budget. However, unlike his March 27th statements to Congress, he told the NASA stakeholder audience that the complex Falcon Heavy configuration “could be used in the future if [NASA can] get through all of [the challenges].” Reading between the lines, Administrator Bridenstine has effectively put the expensive and delay-ridden SLS rocket on notice if its contractors – primarily Boeing – fail to rise to the challenge and accelerate the rocket’s launch debut.
The April 1st comments – made before an audience of major NASA center leaders – are in stark contrast to dozens of comments made by Bridenstine in response to members of Congress on March 27th, in which he repeatedly went to bat for SLS launching Orion on EM-1 while scarcely mentioning commercial alternatives.
Despite the apparent incoherence of Administrator Bridenstine’s continuing comments, the sad – but also promising –
Sitting before the Senate Commerce, Science, and Transportation committee on March 13th, he announced the commercial Orion launch study as a token of recognition that NASA needs to get better at staying on-schedule and on-budget for US taxpayers and Congressional purse string-holders. After the US Vice President challenged NASA to return humans to the Moon with any means necessary by 2024, Bridenstine affirmed that NASA would do everything in its power to meet that charge, including the exploitation of commercial alternatives. In a March 27th hearing before members of Congress with explicit stakes in the SLS rocket’s pork, he barely mentioned commercial alternatives for Orion EM-1, instead focusing on a paired study aiming to accelerate the SLS launch debut schedule while also reiterating his confidence that Boeing and other contractors can rise to the occasion.
In his latest April 1st comments on commercial launch alternatives for Orion’s Moon mission debut, Bridenstine spoke to nearly all of NASA’s major center, program, and directive managers and stuck to the technical facts of the matters at hand. He repeatedly acknowledged that both launching an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to the Moon before the end of 2020 and returning astronauts to its surface by the end of 2024 would be extraordinary challenges and could require far-reaching changes and reforms throughout NASA. He also reaffirmed his intent to ensure that nothing be taken off the table as an option to accomplish those ambitious goals. This included an indication that (in more polite terms, of course) the
We see, in history, that in the past we have had an agenda to get to the Moon and then the resources don’t materialize and it gets canceled, and then we have another agenda to go to the Moon and the resources don’t materialize and it gets canceled. From my perspective, it is my objective to get the resources necessary to accomplish [this goal]. It is also my commitment to make sure that people understand the history here and that we can have a great, ambitious goal, but without the resources, it won’t be accomplished.
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, 04/01/2019


“A whole host of challenges”
The specifics of what the NASA administrator briefly hinted at for a Falcon Heavy launch of EM-1 are spectacular enough to warrant additional discussion. According to Bridenstine, the two-week study NASA conducted essentially concluded that ULA’s Delta IV Heavy rocket was not a practical option for several major reasons. First, it seems that NASA has little to no confidence that Lockheed Martin and its contractors would be able to retrofit EM-1’s Orion and European Service Module (ESM) with the hardware and software needed for on-orbit rendezvous with a boost stage in time for a 2020 launch. Those capabilities were not planned for Orion until EM-3, NET 2024 in an absolute best-case scenario. This would entirely preclude a distributed launch solution, regardless of whether Delta IV Heavy is capable of placing the payloads in orbit.
Even if a rendezvous was on the table, a distributed launch scenario would still be impossible with either two Falcon Heavies or Delta IV Heavies, as both launches would have to occur as close to simultaneously as possible – optimally just a few hours apart. SpaceX has only one pad capable of supporting Falcon Heavy, while ULA’s Delta IV Heavy has two pads, but only one that can launch to the required orbit. A bigger problem: Delta IV Heavy is capable of launching no more than ~28,400 kg (63,000 lb) to an altitude of ~200 km (120 mi), which definitely rules out a Delta IV Heavy launch of the ICPS upper stage (~30,000 kg, 66,000 lb) and could also fall short for Orion/ESM (~26,000 kg, 57,000 lb), assuming that both would need to be launched to an elliptical orbit of 1800 km (1150 mi).

Reddit /u/DoYouWonda actually visualized this potential (but highly improbable) scenario and published a brief abstract analyzing the possibility on March 15th. (Reddit /u/DoYouWonda, minor edits by Teslarati)
Due to NASA’s implied assumption that on-orbit rendezvous of Orion and a booster stage is out of the question and the potential performance shortcomings of Delta IV Heavy, as well as Falcon Heavy’s inability to launch Orion/ESM towards lunar orbit, only one option apparently remains. According to Bridenstine, NASA concluded that a mission profile in which Falcon Heavy places Orion, a service module, and an ICPS upper stage in orbit in a single launch may actually be a serious option – and the only option – for a near-term commercial alternative for Orion’s first operational test flight. The unofficial graphic above offers a rough glimpse of what that massive payload might look like atop Falcon Heavy.
[Finally], there is another solution out there: a Falcon Heavy with an ICPS at the top – talk about strange bedfellows – and an ESM and Orion crew capsule. That ultimately has the ability to potentially – gosh, [NASA Associate Administrator Bill] Gerst is gonna be so mad at me for saying all of this… by the way, none of this was cleared by Gerstenmaier, he’s still the best rocket scientist we have [camera pans to Gerst, laughter], no insult to anyone else in the room – so, at the end of the day, there is a solution here that could potentially work for the future.
It would require time, it would require cost, and there is risk involved, but guess what? If we’re gonna land boots on the Moon in 2024, we have time, and we have the ability to accept some risk and make some modifications. All of that is on the table. There is nothing sacred here that is off the table, and [FH+ICPS+Orion/ESM] is a potential capability that could help us land on the Moon in 2024.
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, 04/01/2019
Combined, the Orion spacecraft, its ESM, and a fueled ICPS boost stage would weigh no less than 56,000 kg (~123,000 lb) at launch, relative to Falcon Heavy’s reported expendable performance of about 64,000 kg (140,000 lb) to Low Earth Orbit (LEO). In other words, it’s possible that Falcon Heavy could effectively do the exact same job as SLS would need to do to perform a nominal Orion EM-1 orbital insertion. However, a huge number of challenges remain for such an exotic Falcon Heavy configuration. Pad 39A would need to be outfitted with an array of systems, including a liquid hydrogen propellant plant and the ability to load Orion and its service module with hypergolic propellant while atop Falcon Heavy and vertical on the pad. To allow for vertical Orion/ESM/ICPS processing and fueling and support the massive weight and height (~95m vs. 70m) of the vehicle, the transporter-erector would need to be heavily modified. Additionally, Falcon Heavy’s aerodynamic characteristics would need to be entirely reanalyzed for such a significantly taller payload fairing.

But, as Bridenstine made clear above, those challenges would be par for the course of accomplishing something as audacious as returning humans to the Moon in less than six years. Whether or not NASA actually pursues or Congress funds such an alternative beyond the drawing board, the cat is now officially out of the bag. A potentially satisfactory replacement for SLS will now hang over the program’s head for the indefinite future, a constant threat in the (quite likely) event that the many SLS/Orion contractors fail – once again – to even loosely adhere to their budget and schedule targets. Falcon Heavy will be waiting.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.
News
SpaceX and Elon Musk explain potential reasons for Starship loss
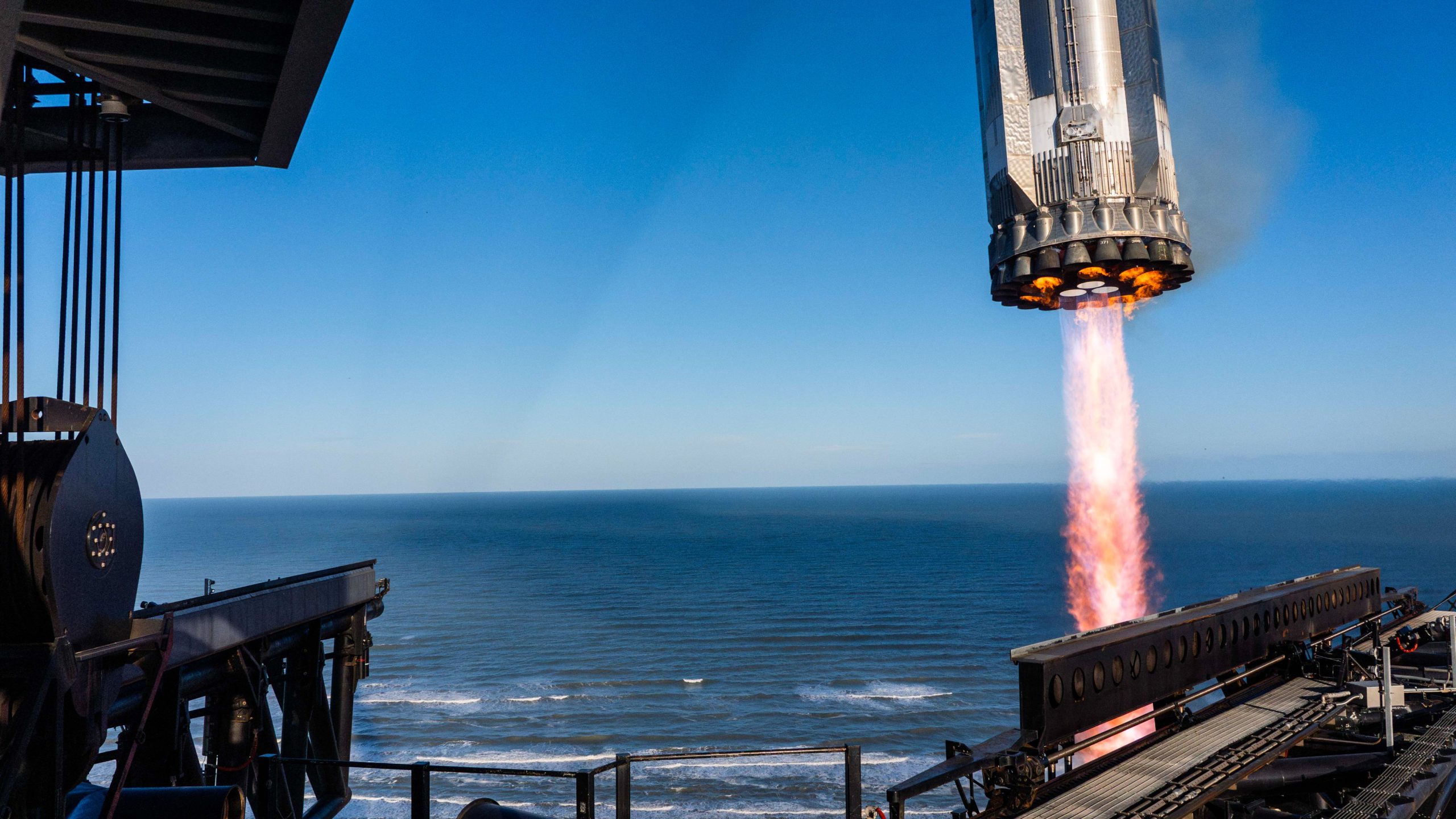

SpaceX and its CEO Elon Musk are starting to shed some light on the potential reasoning for the loss of Starship yesterday, which was lost after a successful launch and catch of the lower-stage booster.
Starship was lost during its ascension, and debris rained down over the Caribbean less than an hour after SpaceX lost all communication with the spacecraft.
A few hours after the launch was over, SpaceX started to shed some light after looking at preliminary data that the rocket left behind.
The company said that a fire developed in the aft section of Starship:
“Following stage separation, the Starship upper stage successfully lit all six Raptor engines and performed its ascent burn to space. Prior to the burn’s completion, telemetry was lost with the vehicle after approximately eight and a half minutes of flight. Initial data indicates a fire developed in the aft section of the ship, leading to a rapid unscheduled disassembly with debris falling into the Atlantic Ocean within the predefined hazard areas.”
Additionally, Musk said that there was some sort of oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall.
The leak was evidently large enough to build more pressure than the vent was able to handle:
🚨Elon Musk has also said an oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could be the cause of the anomaly. https://t.co/BgLkdA9Kk1
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 17, 2025
Some also seemed to recognize evidence of fires throughout the flight of Starship, which is obviously an anomaly:
Unconfirmed but what looks to be fire at the hinge of Starship’s flap. A potential RUD? We await as we get any confirmation from SpaceX.
They do not have comms with the spacecraft as this moment. pic.twitter.com/Cn1EF4AHpv
— Mihir Tripathy (@mihirneal) January 16, 2025
There will be more information regarding the loss of Starship in the coming days and weeks, but Musk already believes that a bit of fire suppression and more volume in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could fix the issue.
“Nothing so far suggests pushing next launch past next month,” he said, so Flight 8 could happen sometime in February.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
SpaceX completes second catch of lower stage, but loses Starship

SpaceX completed its seventh launch of Starship on Thursday, accomplishing a clean liftoff and catch of the first-stage booster. However, the upper stage was lost after its ascent.
The launch took place just a few minutes after 5 p.m. on the East Coast, as the first attempts at getting Starship in the air for the seventh time were delayed by weather both last week and this week.
Conditions were favorable on Thursday as SpaceX looked to follow up a successful campaign by Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos’s company, earlier today.
SpaceX went into the seventh Starship launch with plans for a catch attempt of the first-stage booster, something it attempted and completed during the fifth test launch last year. It decided to skip a catch attempt with the sixth test flight as conditions were not aligned.
For now, SpaceX is extremely selective as to when it attempts catches.
However, it was successful during this attempt, its second completed catch:
🚨 🚀 Here is @SpaceX’s full catch of the Lower Stage Booster from Starship Flight 7! pic.twitter.com/IXIRAGr1Md
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
This flight differed from previous launches as SpaceX rolled out several improvements to the rocket and the processes as it featured plans to do a Starlink deployment simulation and had various adjustments to flap placement and avionics.
These plans were disrupted by the fact that SpaceX lost all communications with Starship about ten minutes into the flight, which the aerospace company confirmed was a result of losing the spacecraft sometime during its ascent.
🚀🚨 Telemetry on Starship has been lost. All comms with the ship have been lost, and SpaceX’s livestream says this is an “anomaly.”
“We are assuming the ship has been lost.” pic.twitter.com/fyyCNuXVRg
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
Although the catch was successful, the loss of the actual rocket seemed to be a huge damper on the entire event. SpaceX confirmed several minutes after the loss of communications that the rocket was destroyed and was lost.
It was its first failure since the second Starship launch in November 2023. SpaceX had no answers for why the rocket was destroyed and lost.
We will keep you updated in the coming days.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
SpaceX confirms next Starship launch target – Here’s when it will take off

SpaceX has confirmed a new target date for the seventh Starship test launch after weather in Texas delayed the first scheduled date for “three or four days.”
The company is now targeting the launch for Monday, January 13, at 4 p.m. CST or 5 p.m. EST. The launch date is not set in stone as any variety of delays could impact this, but SpaceX hopes to finally take off after a delay that pushed it back from January 10.
🚨 STARSHIP LAUNCH DATE: @SpaceX says Starship’s 7th test flight is now targeted for Monday, January 13 at 4pm CST
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 8, 2025
What’s new with this Starship launch
With this being the seventh test launch of Starship, there are several things that the company will change and hope to accomplish. All of these launches are done in preparation for eventually taking flight to Mars, something that will happen next year, according to CEO Elon Musk.
First, SpaceX is rolling out a next-generation ship with “significant upgrades.” Forward flaps have been made smaller and are repositioned away from the heat shield, which will “reduce their exposure to reentry heating.”
There is also a 25 percent increase in propellant volume, a new fuel feedline system for the Raptor vacuum engines, and a better-than-ever propulsion avionics module that will control the valves and reading sensors.
Avionics, as a whole, underwent a redesign and now have more capability and redundancy for missions as they become more complex.
Starlink test
SpaceX is also planning to deploy 10 Starlink simulators that are similar in size and weight to the next-generation Starlink satellites:
“While in space, Starship will deploy 10 Starlink simulators, similar in size and weight to next-generation Starlink satellites as the first exercise of a satellite deploy mission. The Starlink simulators will be on the same suborbital trajectory as Starship, with splashdown targeted in the Indian Ocean. A relight of a single Raptor engine while in space is also planned.”
Ship return and catch
There will be several experiments that have to do with returning Starship and various catch scenarios and sequences. One of which will see “a significant number of tiles be removed to stress-test vulnerable areas across the vehicle.”
The ship’s reentry profile was also intentionally designed to test the structural limits of the flaps while at the point of maximum dynamic pressure during reentry.
Currently, SpaceX did not detail whether it would attempt another catch during this test launch. These are usually game-time decisions.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.


















