

News
NASA’s next Mars rover will pave the way for humans
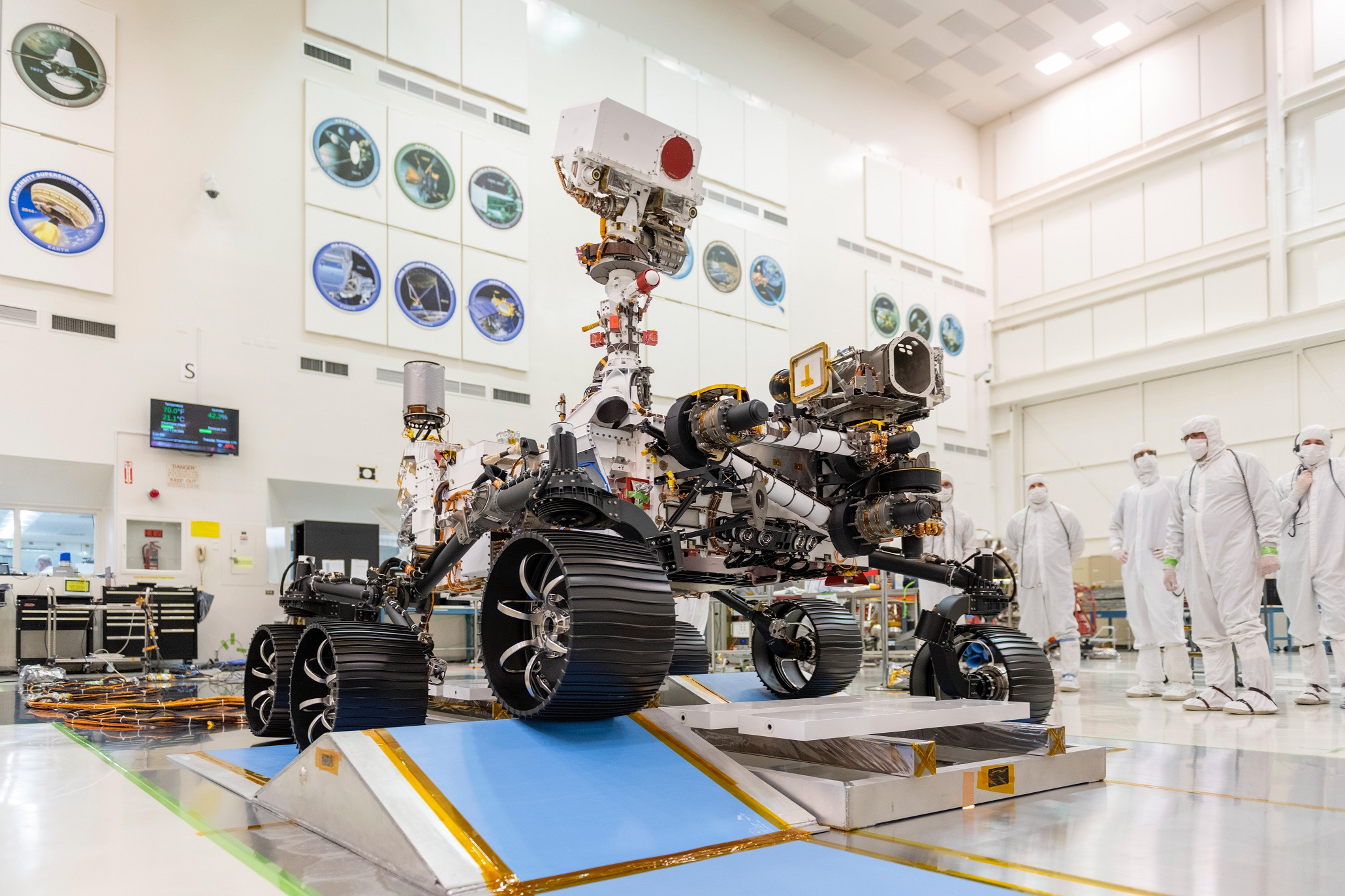
NASA’s Mars 2020 rover is scheduled to land on the red planet in February 2021, and when it does, it will touch down in Jezero Crater, the site of an ancient lake that existed 3.5 billion years ago. The next generation rover, which will get an official name soon, will build on the success of the robotic explorers who came before it by collecting the first samples of Mars for a future return to Earth.
But the new rover will also lay the groundwork for future human exploration by testing new technologies.
The Mars 2020 rover, which looks nearly identical to the Curiosity rover that landed in 2012, will begin its mission exploring Jezero Crater. The six-wheeled rover is equipped with a suite of instruments designed to help it look for signs of life called biosignatures.
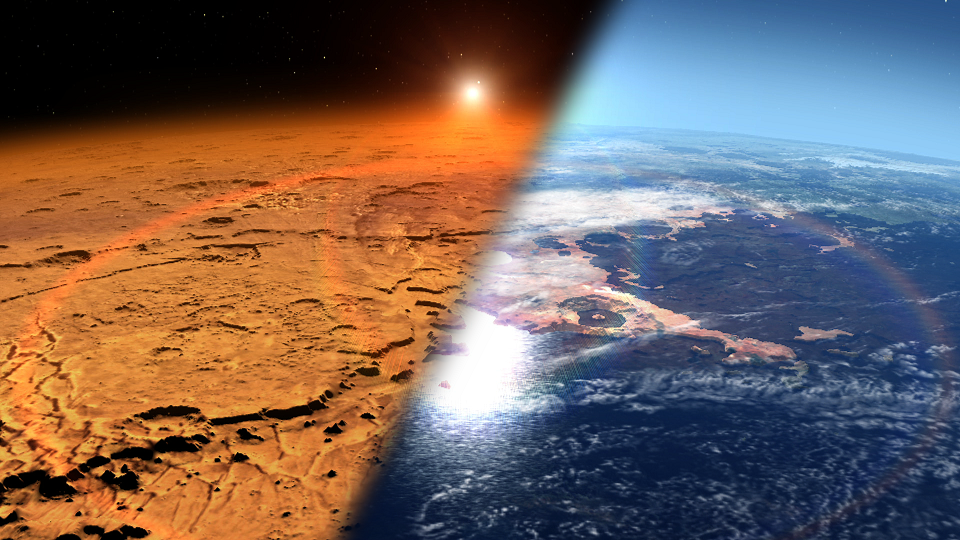

Artist rendition depicting the early Martian environment (right) versus the Mars we see today (left). Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA believes that Mars was habitable sometime in its past. The inhospitable desert-like planet we see today was not always the case. Mars’ once ample atmosphere eroded over time, stripped away by solar particles, resulting in the thin atmosphere we see today.
But so far, we haven’t been able to detect any real signs of ancient life yet. The rover’s team thinks that its specialized suite of instruments will change that.
The twin Mars Exploration Rovers (Spirit and Opportunity) were tasked with finding evidence of water, and they were successful right out of the gate. The Mars Science Laboratory (aka Curiosity) was designed to understand habitability and if the conditions were right for life. Now, the Mars 2020 rover will take that one step further and search for actual signs of life.

Artist rendition depicting the early Martian environment (right) versus the Mars we see today (left). Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
The 2020 rover will do so by drilling into its surroundings and extracting samples that will be returned to Earth at a later time. Returning the samples is a challenge that NASA is already starting to tackle. The agency estimates that the earliest it can send a mission to fetch the rover’s samples would be some time around 2026 or 2027.
In the meantime, 2020 will be busy sciencing the heck out of Mars to search for microbial life as well as testing out technologies that future human missions will rely on.
Here’s how four of those instruments will work.
Terrain Relative Navigation
Landing on Mars is tricky. To date, only about half of the missions attempted have successfully touched down on the red planet. The 2020 rover will be equipped with a specialized feature to help it avoid any potential hazards in the landing zone.
Past missions, like Curiosity, needed a landing spot that was free of debris (like rocks, boulders, etc). But 2020 will be able to navigate around them. That’s because the rover is equipped with a unique lander vision system. This system take pictures during the parachute descent stage. It then compares those images to an onboard map.
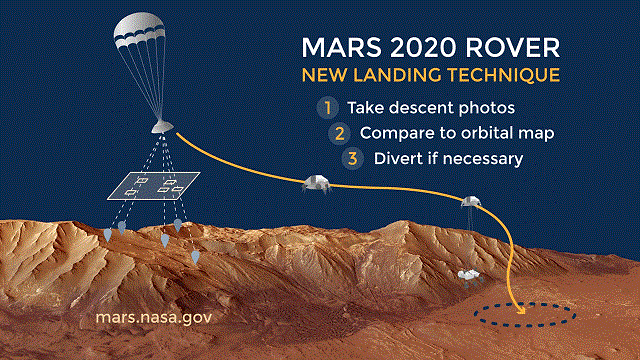
A view of how the terrain-relative navigation works. Credit: NASA/JPL_Caltech
The computer matches the map (which is created from orbital imagery), to create a guide that can identify landmarks such as craters and mountains.
The system then ranks landing sites based on safety, and can even identify a hazard. The Mars 2020 mission will be the first to test out this new system. If all goes well, it will be used on future missions, including human missions to Mars and even the moon.
MOXIE
Astronauts traveling to Mars will need oxygen to breathe and to use as rocket fuel. However, hauling it with the other cargo is expensive and not a viable solution. The Mars 2020 rover is equipped with an instrument on called the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE for short).
MOXIE will convert carbon dioxide (a gas that’s abundant on Mars) into the oxygen, which astronauts can use as needed. 2020 is equipped with a small, prototype version of the equipment needed for future human missions.
The team will study how the experiment performs and use that data to scale up the technology to use on subsequent missions. But how will it work?
MOXIE can only run for a few hours at a time, and only about once a month. (That’s because the system uses a full day’s worth of rover power each time it runs.) Humans use about 20 grams per hour of oxygen and MOXIE can only produce about half of that.
In order to support a crew of 4-6 astronauts and be able to generate propellant, future iterations of MOXIE will need to produce about 200 times that amount of oxygen.
MEDA
The Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer, aka MEDA, is a suite of sensors designed to study the Martian weather, as well as dust and radiation and how they change over the Martian seasons.
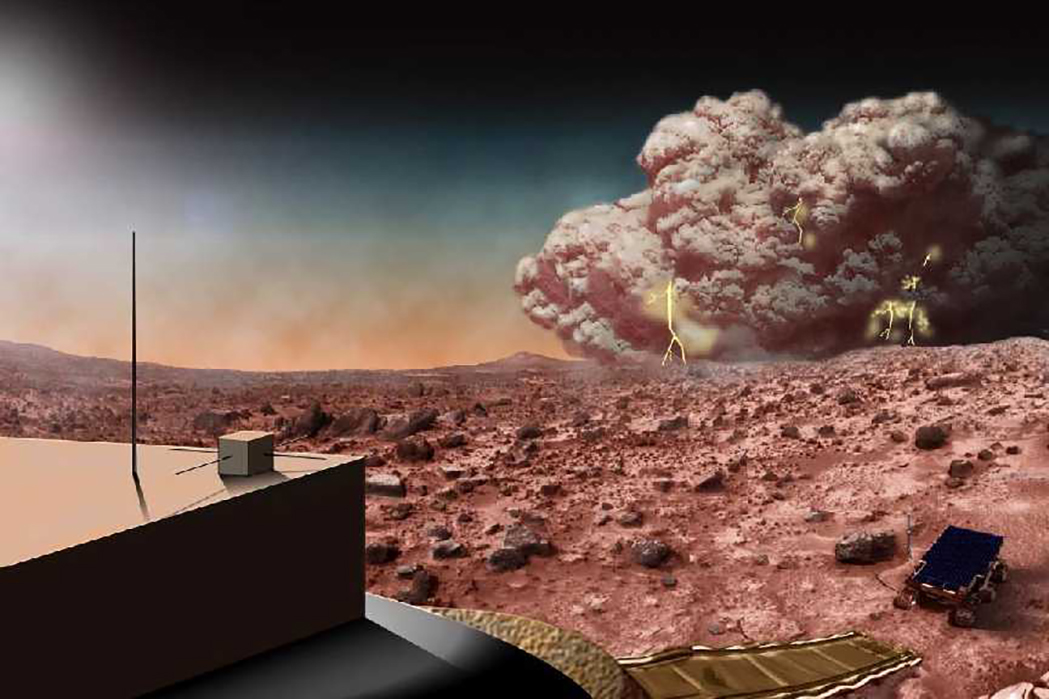

NASA is trying to better understand dust storms and other Martian weather phenomenon. Credit: NASA
Day and nighttime temperatures on Mars can fluctuate by as much as 80 or 90 degrees. MEDA will help scientists track those changes as well as measure radiation from the surface, to understand how much the sun heats the air. This solar heating causes changes in the Martian wind and can help scientists better understand the Martian water cycle.
Understanding the current weather patterns and environment could also lead to a better understanding of Mars’s history and shed light on how it transitioned from a warm, habitable planet into the dusty, cold desert we see today.
RIMFAX
The Mars 2020 rover will be equipped with a ground-penetrating radar instrument: Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment, or RIMFAX.
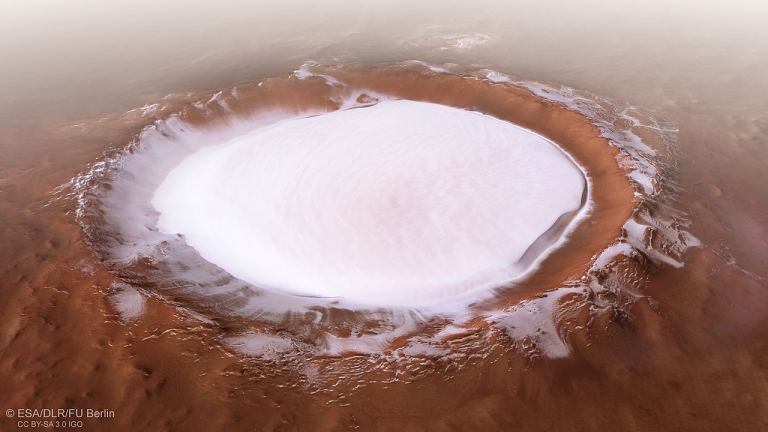

The Korolev crater on Mars as seen by Mars Express. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin
Scientists hope that RIMAX will help them study the history of Jezero Crater by peering below the surface. With the instrument’s help, scientists will be able to look at subsurface rock and ice. To date, only orbital observations have been made of the Martian polar ice, but this will increase our understanding of the planet’s inner geology.
The Mars 2020 rover is scheduled to launch in July of 2020, and will land on the Martian surface six months later. If all goes according to plan, we may finally be able to answer the question of whether or not Mars once hosted life.
News
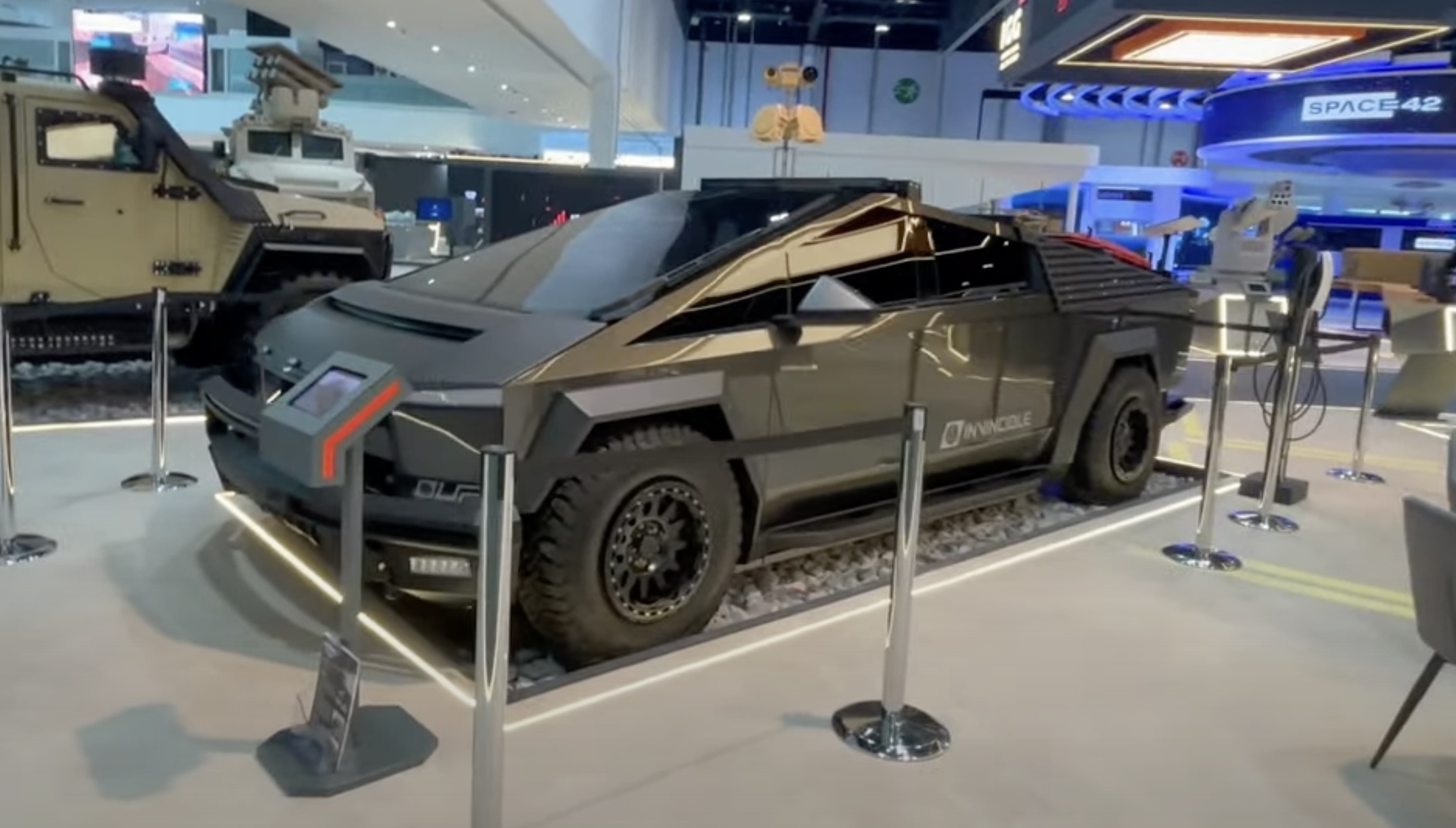
Armored Tesla Cybertruck “War Machine” debuts at Defense Expo 2025
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.

Temporibus autem quibusdam et aut officiis debitis aut rerum necessitatibus saepe eveniet ut et voluptates repudiandae sint et molestiae non recusandae. Itaque earum rerum hic tenetur a sapiente delectus, ut aut reiciendis voluptatibus maiores alias consequatur aut perferendis doloribus asperiores repellat.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
“Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat”
Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit, sed quia consequuntur magni dolores eos qui ratione voluptatem sequi nesciunt.
Et harum quidem rerum facilis est et expedita distinctio. Nam libero tempore, cum soluta nobis est eligendi optio cumque nihil impedit quo minus id quod maxime placeat facere possimus, omnis voluptas assumenda est, omnis dolor repellendus.
Nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
Neque porro quisquam est, qui dolorem ipsum quia dolor sit amet, consectetur, adipisci velit, sed quia non numquam eius modi tempora incidunt ut labore et dolore magnam aliquam quaerat voluptatem. Ut enim ad minima veniam, quis nostrum exercitationem ullam corporis suscipit laboriosam, nisi ut aliquid ex ea commodi consequatur.
At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti quos dolores et quas molestias excepturi sint occaecati cupiditate non provident, similique sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollitia animi, id est laborum et dolorum fuga.
Quis autem vel eum iure reprehenderit qui in ea voluptate velit esse quam nihil molestiae consequatur, vel illum qui dolorem eum fugiat quo voluptas nulla pariatur.
News
Tesla Megapacks chosen for 548 MWh energy storage project in Japan
Tesla plans to supply over 100 Megapack units to support a large stationary storage project in Japan, making it one of the country’s largest energy storage facilities.

Tesla’s Megapack grid-scale batteries have been selected to back an energy storage project in Japan, coming as the latest of the company’s continued deployment of the hardware.
As detailed in a report from Nikkei this week, Tesla plans to supply 142 Megapack units to support a 548 MWh storage project in Japan, set to become one of the country’s largest energy storage facilities. The project is being overseen by financial firm Orix, and it will be located at a facility Maibara in central Japan’s Shiga prefecture, and it aims to come online in early 2027.
The deal is just the latest of several Megapack deployments over the past few years, as the company continues to ramp production of the units. Tesla currently produces the Megapack at a facility in Lathrop, California, though the company also recently completed construction on its second so-called “Megafactory” in Shanghai China and is expected to begin production in the coming weeks.
READ MORE ON TESLA MEGAPACKS: Tesla Megapacks help power battery supplier Panasonic’s Kyoto test site
Tesla’s production of the Megapack has been ramping up at the Lathrop facility since initially opening in 2022, and both this site and the Shanghai Megafactory are aiming to eventually reach a volume production of 10,000 Megapack units per year. The company surpassed its 10,000th Megapack unit produced at Lathrop in November.
During Tesla’s Q4 earnings call last week, CEO Elon Musk also said that the company is looking to construct a third Megafactory, though he did not disclose where.
Last year, Tesla Energy also had record deployments of its Megapack and Powerwall home batteries with a total of 31.4 GWh of energy products deployed for a 114-percent increase from 2023.
Other recently deployed or announced Megapack projects include a massive 600 MW/1,600 MWh facility in Melbourne, a 75 MW/300 MWh energy storage site in Belgium, and a 228 MW/912 MWh storage project in Chile, along with many others still.
What are your thoughts? Let me know at zach@teslarati.com, find me on X at @zacharyvisconti, or send us tips at tips@teslarati.com.
Tesla highlights the Megapack site replacing Hawaii’s last coal plant
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
News
Elon Musk responds to Ontario canceling $100M Starlink deal amid tariff drama
Ontario Premier Doug Ford said, opens new tab on February 3 that he was “ripping up” his province’s CA$100 million agreement with Starlink in response to the U.S. imposing tariffs on Canadian goods.

Elon Musk company SpaceX is set to lose a $100 million deal with the Canadian province of Ontario following a response to the Trump administration’s decision to apply 25 percent tariffs to the country.
Starlink, a satellite-based internet service launched by the Musk entity SpaceX, will lose a $100 million deal it had with Ontario, Premier Doug Ford announced today.
Starting today and until U.S. tariffs are removed, Ontario is banning American companies from provincial contracts.
Every year, the Ontario government and its agencies spend $30 billion on procurement, alongside our $200 billion plan to build Ontario. U.S.-based businesses will…
— Doug Ford (@fordnation) February 3, 2025
Ford said on X today that Ontario is banning American companies from provincial contracts:
“We’ll be ripping up the province’s contract with Starlink. Ontario won’t do business with people hellbent on destroying our economy. Canada didn’t start this fight with the U.S., but you better believe we’re ready to win it.”
It is a blow to the citizens of the province more than anything, as the Starlink internet constellation has provided people in rural areas across the globe stable and reliable access for several years.
Musk responded in simple terms, stating, “Oh well.”
Oh well https://t.co/1jpMu55T6s
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 3, 2025
It seems Musk is less than enthused about the fact that Starlink is being eliminated from the province, but it does not seem like all that big of a blow either.
As previously mentioned, this impacts citizens more than Starlink itself, which has established itself as a main player in reliable internet access. Starlink has signed several contracts with various airlines and maritime companies.
It is also expanding to new territories across the globe on an almost daily basis.
With Mexico already working to avoid the tariff situation with the United States, it will be interesting to see if Canada does the same.
The two have shared a pleasant relationship, but President Trump is putting his foot down in terms of what comes across the border, which could impact Americans in the short term.



















