
SpaceX
SpaceX builds new orbital Starship sections as Starhopper loses its engine
Amidst the growing buzz centered around the imminent second launch of Falcon Heavy, SpaceX’s South Texas team has continued to work on Starhopper and the first orbital Starship prototype. wrapping up the first major tests of the former and making new progress on the latter’s aeroshell.
For unknown reasons, SpaceX technicians uninstalled Starhopper’s Raptor – the second full-scale engine ever built – shortly after the vehicle’s first true hop test and proceeded to package it up for shipment elsewhere, likely McGregor’s test facilities or the Hawthorne factory. Simultaneously, the third completed Raptor (SN03) was recently installed in McGregor according to photos and observations published by NASASpaceflight.com, preparing to continue to the engineering verification tests that began in February. Once those tests are complete and the engine design is modified to account for the lessons learned with Raptor SN01, SpaceX’s next step will be to begin ramping Raptor production in preparation for multi-engine Starhopper testing and – eventually – the completion of the first orbit-capable Starship prototype.
Needless to say, SpaceX is juggling a lot of interconnected projects in an effort to speed its Starship/Super Heavy (formerly BFR) development program, none of which are being discussed by the company in more than a cursory manner. What follows is thus meant to be an informed but speculative estimate of what is currently going on and what is next for BFR.
Starhopper slips the surly bonds
Over the course of the last two weeks, SpaceX has been almost continuously testing the first integrated Starship prototype, a partial-fidelity vehicle known as Starhopper. The testing primarily involved almost a dozen wet dress rehearsals (WDRs) in which the rocket was filled with some quantity of liquid oxygen and methane propellant and helium for pressurization as engineers and technicians worked through several bugs preventing Raptor from safely operating. According to CEO Elon Musk, some form of ice – potentially methane, oxygen, or even water – was forming in or around parts known as “prevalves”, likely referring to valves involved in the process of supply rocket engines with the right amount of fuel and oxidizer.
Less than 24 hours later, those valve issues were apparently solved as Starhopper’s Raptor ignited for the first time in a spectacular nighttime fireball. 48 hours after that first ignition, SpaceX once again fueled Starhopper and ignited its Raptor engine, lifting a spectacular handful of feet into the air before reaching the end of its very short tethers. According to Musk, the first Raptor ignition was completed with “all systems green”. After the second test, no additional comments were made. Less than three days later, SpaceX technicians uninstalled Starhopper’s Raptor (SN02) and shipped it somewhere offsite, indicating that it may have suffered a fault similar to the one that caused relatively minor damage to Raptor SN01 at the end of its February test campaign. Regardless, it appears that this development will keep Starhopper grounded for the indefinite future barring the imminent shipment of Raptor SN04 or the completion of SN01’s refurbishment.
The Raptor pack grows
Starhopper’s unplanned grounding ties
While the exact strategy behind SpaceX’s Raptor and BFR propulsion development programs
Regardless, the somewhat buggy behavior exhibited by the integrated Raptor and Starhopper indicate the obvious: both are fairly immature hardware still in some form of development, be it the late (Raptor) or the very earliest stages (Starhopper). By performing even more testing and continuing to optimize and gain familiarity with the hardware at hand, the fairly predictable process of development will arrive at more or less finished products.


Starship’s first orbital prototype
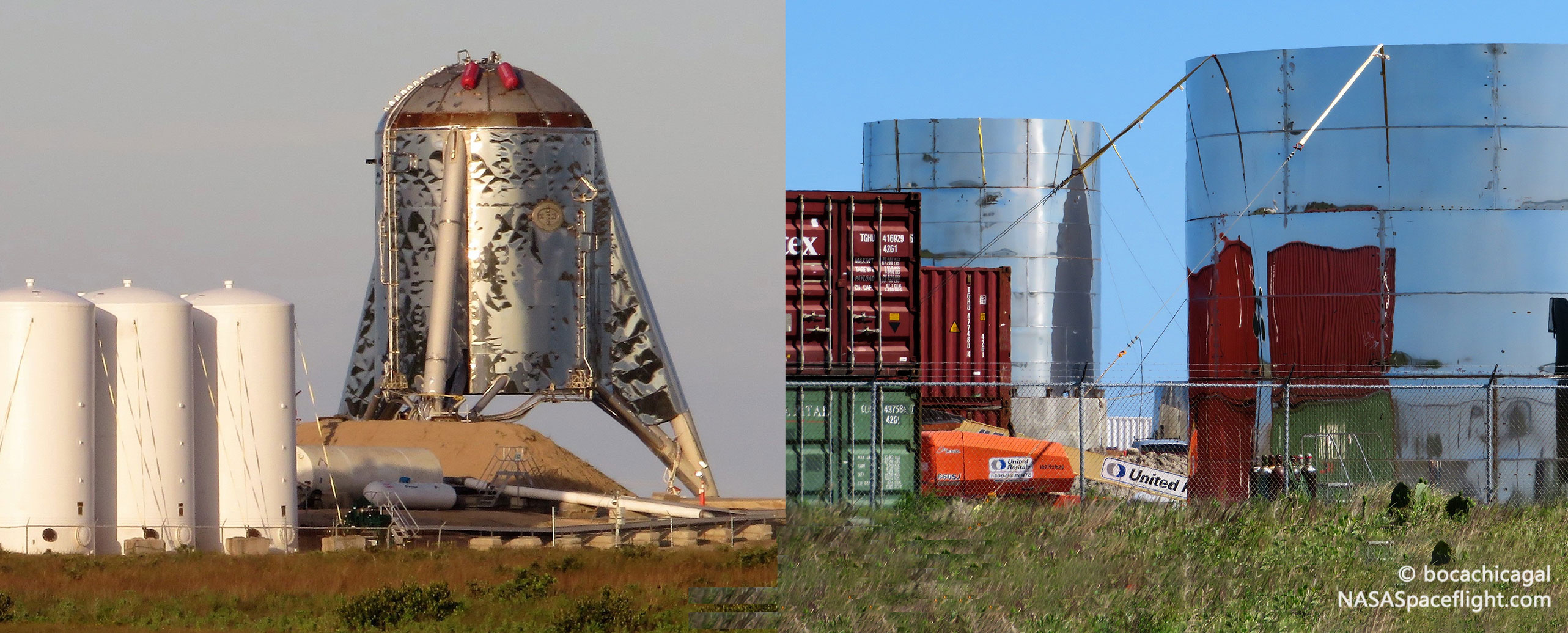
Last but not least, work continues on what will hopefully become the first orbit-capable Starship prototype, built in full-scale out of sheets of stainless steel that are far thinner than the metal used to construct Starhopper. This, too, is a normal process of development – as progress is made, prototypes will gradually lose an emergency cushion of performance margins, a bit like a sculptor starting with a solid block of marble and whittling it down to a work of art. Starhopper is that marble block, with inelegant, rough angles and far more material bulk than truly necessary.
As seen above, the orbital prototype – just the second in a presumably unfinished series – is already dramatically more refined. Instead of the first facade-like nose cone built for Starhopper, Starship’s nose section is being built out of smoothly tapered stainless steel panels that appear identical to those used to assemble the rocket’s growing aeroshell and tankage. As of now, there are five publicly visible Starship sections in various forms of fabrication, followed by a half-dozen or so tank dome segments waiting to be welded together as finished bulkheads.
Intriguingly, the only quasi-public official render of SpaceX’s steel Starship features visible sections very similar to those seen on the orbital prototype’s welded hull. They aren’t all visible in the render, but those that are are a distinct match to the aspect ratio of the welded sections visible in South Texas.

Extrapolating from this observation, Starship, as rendered, is comprised of approximately 16 large cylinder sections and 4-8 tapered nose sections. Based on the real orbital prototype, each large section is 9m in diameter and ~2.5m tall. Assuming Starship is 55 meters (180 ft) tall, this would translate into 22 2.5m sections, a nearly perfect fit with what is shown in the official render. Back in South Texas, SpaceX has 6 tapered sections and 7 cylinder sections in work, meaning that they would reach around 32.5m (~105 ft) – about 60% of a Starship hull – if stacked today.
If we assume that SpaceX follows Falcon procedures to build the seven-Raptor thrust structure separately (~2 sections) and excludes most of the cargo bay (~2-3 sections) on the first orbit-capable Starship, those ~13 in-work sections could be just a tapered nose cone away from the prototype’s full aeroshell. Time will tell…
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes.
News
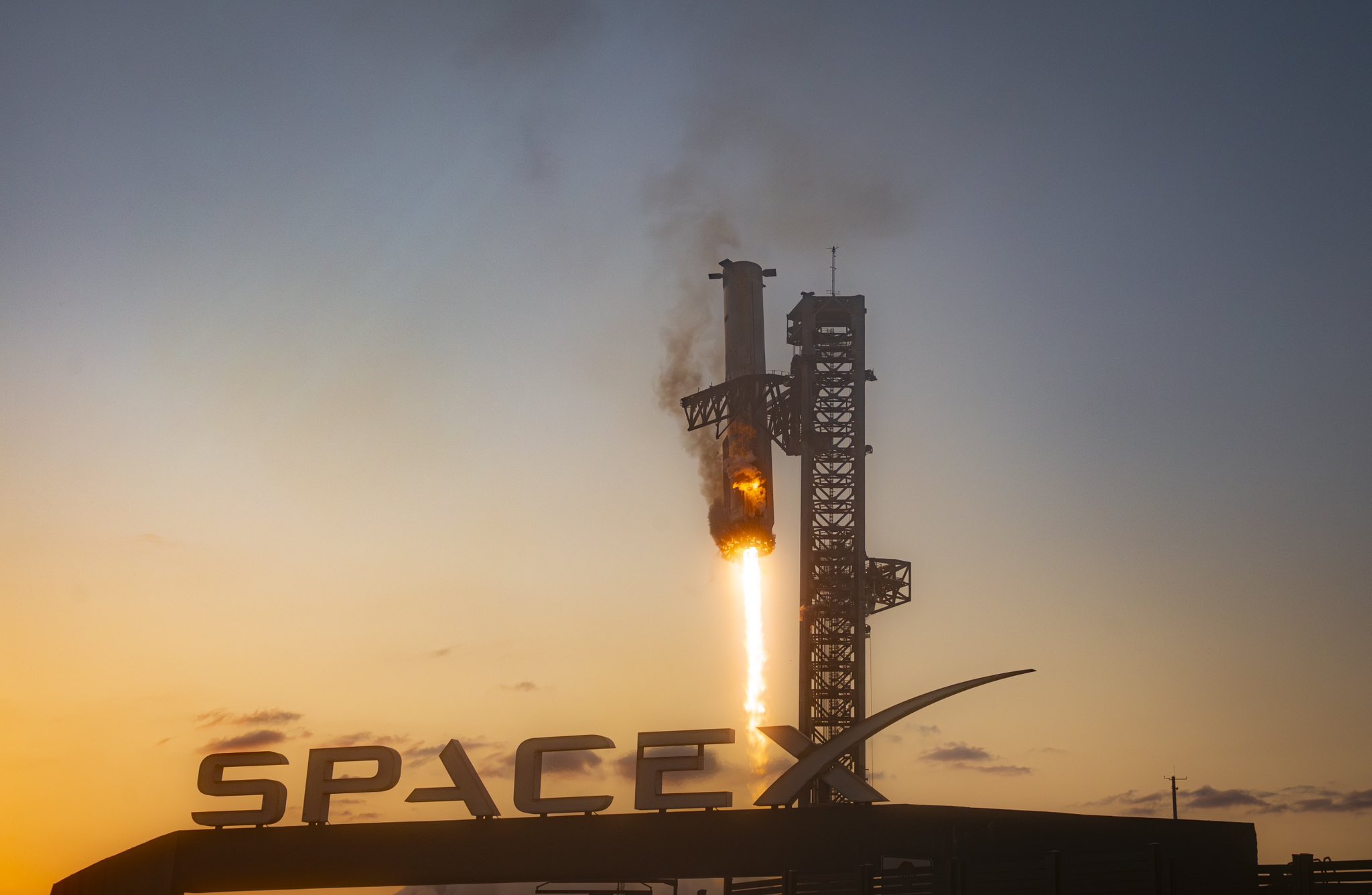
SpaceX and Elon Musk explain potential reasons for Starship loss

SpaceX and its CEO Elon Musk are starting to shed some light on the potential reasoning for the loss of Starship yesterday, which was lost after a successful launch and catch of the lower-stage booster.
Starship was lost during its ascension, and debris rained down over the Caribbean less than an hour after SpaceX lost all communication with the spacecraft.
A few hours after the launch was over, SpaceX started to shed some light after looking at preliminary data that the rocket left behind.
The company said that a fire developed in the aft section of Starship:
“Following stage separation, the Starship upper stage successfully lit all six Raptor engines and performed its ascent burn to space. Prior to the burn’s completion, telemetry was lost with the vehicle after approximately eight and a half minutes of flight. Initial data indicates a fire developed in the aft section of the ship, leading to a rapid unscheduled disassembly with debris falling into the Atlantic Ocean within the predefined hazard areas.”
Additionally, Musk said that there was some sort of oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall.
The leak was evidently large enough to build more pressure than the vent was able to handle:
🚨Elon Musk has also said an oxygen or fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could be the cause of the anomaly. https://t.co/BgLkdA9Kk1
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 17, 2025
Some also seemed to recognize evidence of fires throughout the flight of Starship, which is obviously an anomaly:
Unconfirmed but what looks to be fire at the hinge of Starship’s flap. A potential RUD? We await as we get any confirmation from SpaceX.
They do not have comms with the spacecraft as this moment. pic.twitter.com/Cn1EF4AHpv
— Mihir Tripathy (@mihirneal) January 16, 2025
There will be more information regarding the loss of Starship in the coming days and weeks, but Musk already believes that a bit of fire suppression and more volume in the cavity above the ship engine firewall could fix the issue.
“Nothing so far suggests pushing next launch past next month,” he said, so Flight 8 could happen sometime in February.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
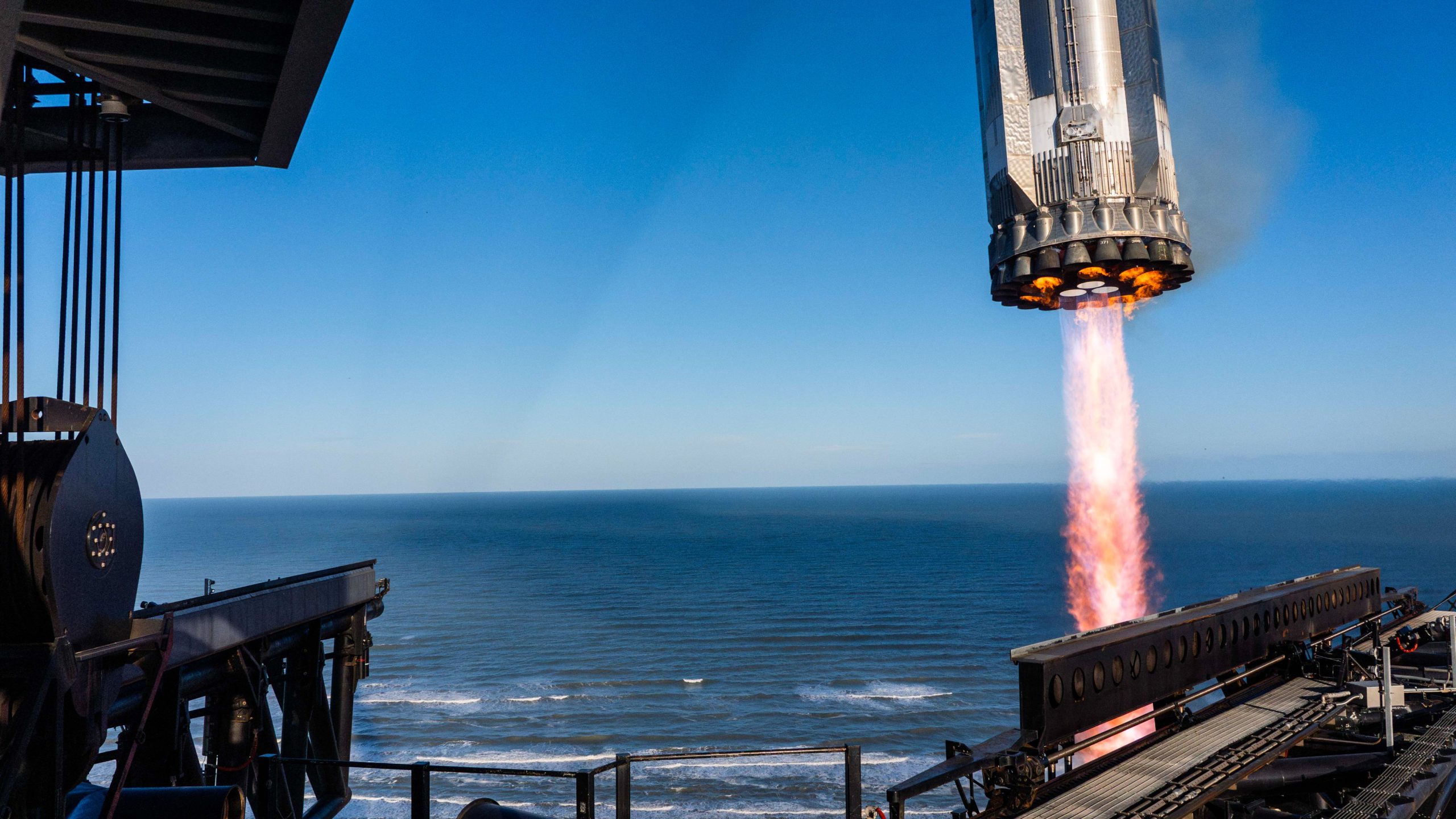
SpaceX completes second catch of lower stage, but loses Starship

SpaceX completed its seventh launch of Starship on Thursday, accomplishing a clean liftoff and catch of the first-stage booster. However, the upper stage was lost after its ascent.
The launch took place just a few minutes after 5 p.m. on the East Coast, as the first attempts at getting Starship in the air for the seventh time were delayed by weather both last week and this week.
Conditions were favorable on Thursday as SpaceX looked to follow up a successful campaign by Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos’s company, earlier today.
SpaceX went into the seventh Starship launch with plans for a catch attempt of the first-stage booster, something it attempted and completed during the fifth test launch last year. It decided to skip a catch attempt with the sixth test flight as conditions were not aligned.
For now, SpaceX is extremely selective as to when it attempts catches.
However, it was successful during this attempt, its second completed catch:
🚨 🚀 Here is @SpaceX’s full catch of the Lower Stage Booster from Starship Flight 7! pic.twitter.com/IXIRAGr1Md
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
This flight differed from previous launches as SpaceX rolled out several improvements to the rocket and the processes as it featured plans to do a Starlink deployment simulation and had various adjustments to flap placement and avionics.
These plans were disrupted by the fact that SpaceX lost all communications with Starship about ten minutes into the flight, which the aerospace company confirmed was a result of losing the spacecraft sometime during its ascent.
🚀🚨 Telemetry on Starship has been lost. All comms with the ship have been lost, and SpaceX’s livestream says this is an “anomaly.”
“We are assuming the ship has been lost.” pic.twitter.com/fyyCNuXVRg
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 16, 2025
Although the catch was successful, the loss of the actual rocket seemed to be a huge damper on the entire event. SpaceX confirmed several minutes after the loss of communications that the rocket was destroyed and was lost.
It was its first failure since the second Starship launch in November 2023. SpaceX had no answers for why the rocket was destroyed and lost.
We will keep you updated in the coming days.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
SpaceX confirms next Starship launch target – Here’s when it will take off

SpaceX has confirmed a new target date for the seventh Starship test launch after weather in Texas delayed the first scheduled date for “three or four days.”
The company is now targeting the launch for Monday, January 13, at 4 p.m. CST or 5 p.m. EST. The launch date is not set in stone as any variety of delays could impact this, but SpaceX hopes to finally take off after a delay that pushed it back from January 10.
🚨 STARSHIP LAUNCH DATE: @SpaceX says Starship’s 7th test flight is now targeted for Monday, January 13 at 4pm CST
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 8, 2025
What’s new with this Starship launch
With this being the seventh test launch of Starship, there are several things that the company will change and hope to accomplish. All of these launches are done in preparation for eventually taking flight to Mars, something that will happen next year, according to CEO Elon Musk.
First, SpaceX is rolling out a next-generation ship with “significant upgrades.” Forward flaps have been made smaller and are repositioned away from the heat shield, which will “reduce their exposure to reentry heating.”
There is also a 25 percent increase in propellant volume, a new fuel feedline system for the Raptor vacuum engines, and a better-than-ever propulsion avionics module that will control the valves and reading sensors.
Avionics, as a whole, underwent a redesign and now have more capability and redundancy for missions as they become more complex.
Starlink test
SpaceX is also planning to deploy 10 Starlink simulators that are similar in size and weight to the next-generation Starlink satellites:
“While in space, Starship will deploy 10 Starlink simulators, similar in size and weight to next-generation Starlink satellites as the first exercise of a satellite deploy mission. The Starlink simulators will be on the same suborbital trajectory as Starship, with splashdown targeted in the Indian Ocean. A relight of a single Raptor engine while in space is also planned.”
Ship return and catch
There will be several experiments that have to do with returning Starship and various catch scenarios and sequences. One of which will see “a significant number of tiles be removed to stress-test vulnerable areas across the vehicle.”
The ship’s reentry profile was also intentionally designed to test the structural limits of the flaps while at the point of maximum dynamic pressure during reentry.
Currently, SpaceX did not detail whether it would attempt another catch during this test launch. These are usually game-time decisions.
Need accessories for your Tesla? Check out the Teslarati Marketplace:
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-cybertruck-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-y-accessories
- https://shop.teslarati.com/collections/tesla-model-3-accessories
Please email me with questions and comments at joey@teslarati.com. I’d love to chat! You can also reach me on Twitter @KlenderJoey, or if you have news tips, you can email us at tips@teslarati.com.


















